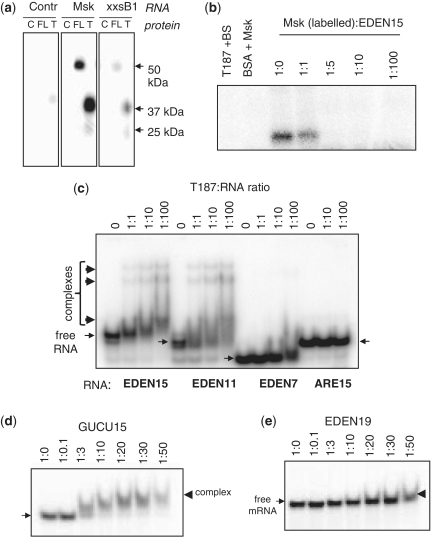
Figure 2.
The first 187 amino acids of CELF1 are sufficient for specific binding to natural and synthetic binding sites. (a) UV-crosslinking of BSA control (C), full length CELF1 (FL), T353 (T) with radioactive maskin 3′-UTR (Msk), a truncated cyclinB1 3′-UTR (xxsB1) and a Control RNA (Bluescript polylinker transcript). Sizes of crosslinked bands are indicated. (b) UV-Crosslinking competition assay. The maskin 3′-UTR was competed with synthetic EDEN15. Radioactive control RNA (Bluescript: BS) or maskin 3′-UTR with EDEN15 in the indicated molar ratios were incubated with T187 and covalently crosslinked using by UV light. (c) Gel retardation assay with T187 EDEN15, EDEN11 and EDEN7, as well as with the AU rich element (ARE15) incubated in buffer A. An amount of 50 nM of RNA end labelled with γ-P32-ATP was incubated with increasing concentration of t187 protein, ratio RNA: protein from 1:0 to 1:100. Slender arrows indicate free RNA, thick arrows complexes induced by the protein. (d) Gel retardation of 45 nM GUCU15 with increasing concentrations of T187 in buffer B. (e) Gel retardation of 45 nM EDEN19 with increasing concentrations of T187 in buffer B.