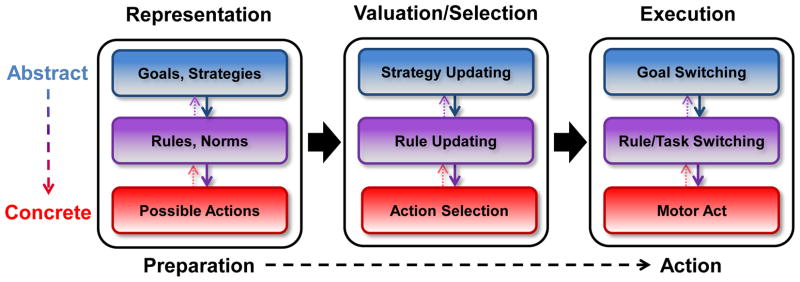
Figure 2. A schematic, integrative model of goal-directed decision making.
Each stage of decision making requires control processes at multiple levels of abstraction. Competing actions, rules and strategies are selected via a value-comparison process, in which cognitive control coordinates the assignment of action values based on the representations of superordinate goals, objectives, and strategies.