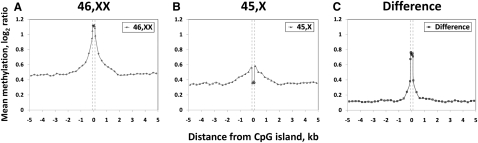
Figure 3.
Differential methylation between active and inactive X chromosomes occurs specifically at CpG islands. Each panel shows a composite plot of mean methylation levels within and flanking 3060 CGIs on the X chromosome in (A) 46,XX females; (B) 45,X Turner syndrome cases, corresponding to the Xa; and (C) the difference between these two groups, corresponding to the Xi. Three thousand sixty CGIs defined using epigenetic criteria (Bock et al. 2007) were analyzed. Those separated by <500 bp (n = 726) were merged into single regions, and the mean methylation level both within CGIs, and +5 kb and −5 kb was calculated. The apparent increase in methylation in flanking regions in 46,XX individuals is likely due to the clustering of CGIs on the X chromosome, which results in neighboring CGIs being sampled in the 5-kb flanking regions (10% of CGIs are separated by <1 kb, 36% by <5 kb). (Gray dashes) Borders of the CGIs. Mean methylation within CGIs was calculated by assigning probes into 10 windows proportional to the length of each CGI. Mean methylation in flanking regions was plotted in 250-bp windows. Underlying mean log2 values with variance and associated P-values are shown in Supplemental Table 2.