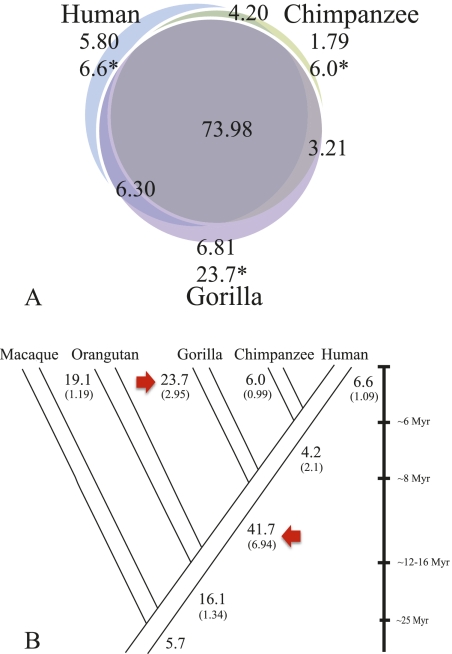
Figure 3.
Segmental duplication distributions. (A) SDs (>20 kb) were classified as lineage-specific or shared based on a three-way comparison of human, chimpanzee, and gorilla genomes. The inclusion of gorilla suggests that most SDs are shared among humans and African apes but not with Asian apes (Supplemental Note; Marques-Bonet et al. 2009a). Numbers are in megabase pairs; all SDs were validated by interspecies arrayCGH; (*) megabase pairs adjusted for copy number. (B) Using parsimony, we assigned the number of megabase pairs to different terminal and ancestral branches in the human-ape phylogeny. The copy-number-corrected megabase pairs are shown (bold type) and a calculated rate of megabase pairs/million years (in brackets) is estimated. A simple maximum-likelihood ratio test showed a dramatic SD burst in the African ape ancestor and in the common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees. The gorilla lineage-specific rate is greater than any other hominid.