Figure 8.
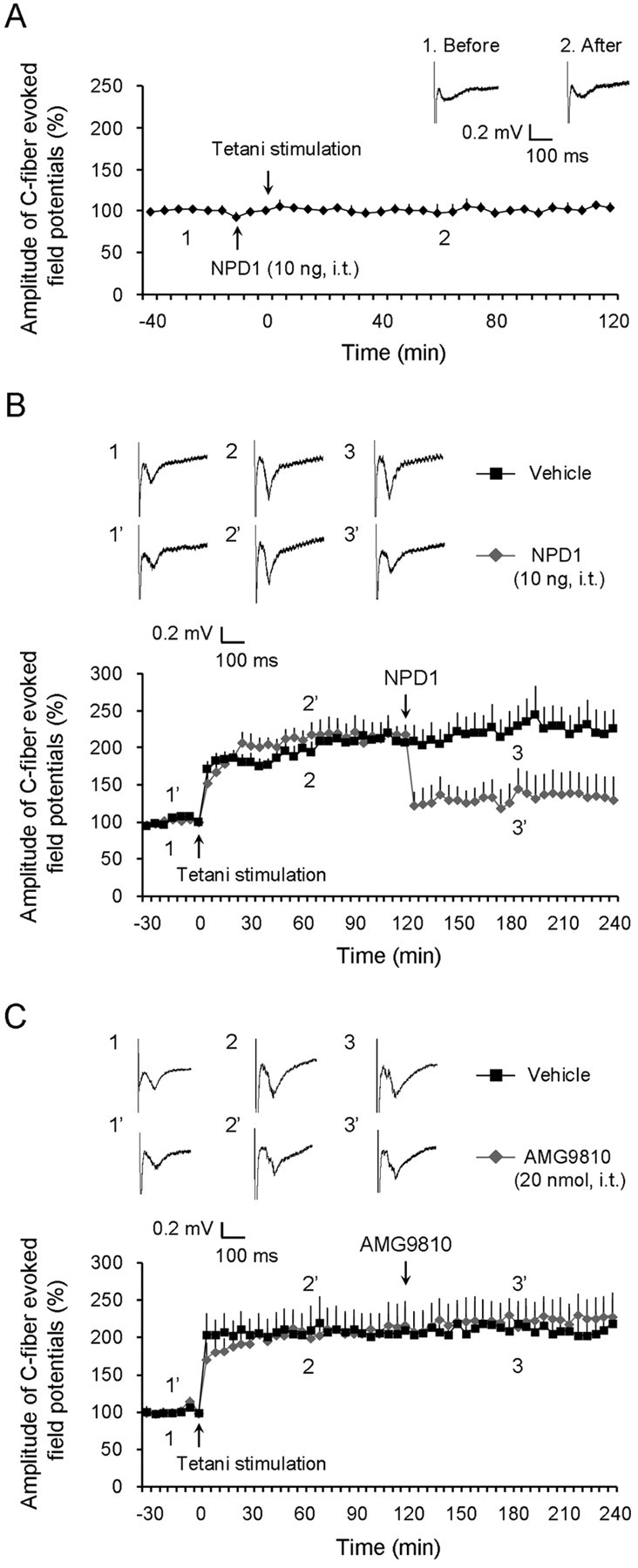
Prevention and reversal of spinal LTP by intrathecal NPD1 and no reversal of spinal LTP by intrathecal AMG9810. A, Prevention of LTP of C-fiber-evoked field potentials in the dorsal horn of anesthetized WT mice by NPD1 (10 ng, i.t.). Top traces are C-fiber-evoked field potentials in the dorsal horn in NPD1-treated mice before (1) and after (2) conditioning tetanic stimulation. n = 5 mice. B, Reversal of LTP of C-fiber-evoked field potentials in the dorsal horn of anesthetized WT mice by NPD1 (10 ng, i.t.), administrated 2 h after LTP induction. Top traces are C-fiber-evoked spinal field potentials in vehicle- and NPD1-treated mice before LTP induction (1 and 1′), after LTP induction (2 and 2′), and after NPD1 treatment (3 and 3′). *p < 0.05 (vehicle vs NPD1, two-way ANOVA, n = 5). C, No reversal of LTP of C-fiber-evoked field potentials in the dorsal horn of anesthetized WT mice by AMG9810 (20 nmol, i.t.), administrated 2 h after LTP induction by tetani (4 trains of tetanic stimulation). Top traces are C-fiber-evoked spinal field potentials in vehicle- and NPD1-treated mice before LTP induction (1 and 1′), after LTP induction (2 and 2′), and after NPD1 treatment (3 and 3′). n = 5 mice for AMG9801 and 4 mice for vehicle (10% DMSO). All the data shown are mean ± SEM.
