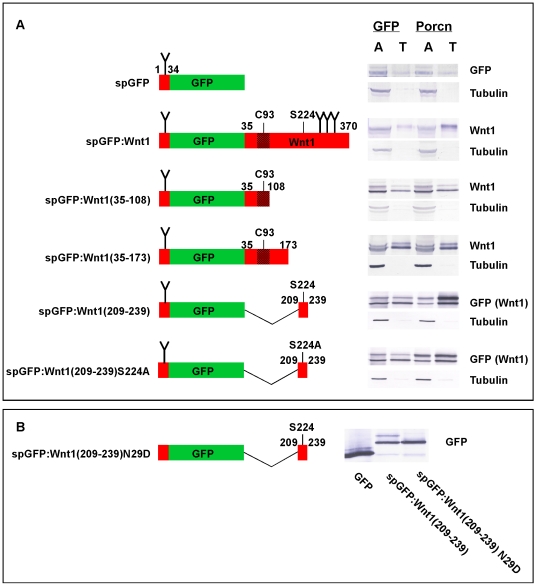
Figure 9. Porcn overexpression increases the hydrophobicity of spGFP∶Wnt1(209–239), but not spGFP∶Wnt1(35–108) in the TX-114 assay.
Panel A: 293T cells were transfected with spGFP-tagged peptides in the presence of GFP (control) or mPorcD. A diagram of tested spGFP∶Wnt1 fusions is shown on the left. Wnt1 sequences are indicated in red while GFP sequences are indicated in green. Indicated numbers correspond to the residue position in full-length Wnt1. Consensus sites for the addition of N-linked carbohydrates are shown by a “Y”. The stippled region surrounding C93 indicates the antigen that was used to raise our monoclonal antibodies against Wnt1. Cells were incubated overnight, lysed, and extracted with TX-114 before analysis by SDS-PAGE/Western blot. spGFP∶Wnt1 fusions were detected with either Wnt1 or GFP antibodies. Blotting with ß-tubulin antibodies served as a control for the extraction as we have previously shown that ß-tubulin preferentially partitions to the aqueous phase. When co-transfected with GFP, all of the fusion proteins are found in both aqueous (A) and detergent/Triton X-114 (T) phases. The presence of ectopic Porcn promotes the partitioning of spGFP∶Wnt1, spGFP∶Wnt1 (209–239), and spGFP∶Wnt1 (209–239) S224A, but not spGFP∶Wnt1 (35–108) or spGFP∶Wnt1 (35–173) into the hydrophobic phase, indicating that 1) Porcn promotes the hydrophobic modification of a 31 residue peptide containing S224 2) that at least one additional site for the modification of Wnt by Porcn is likely to exist within the 31 residue peptide. These experiments were performed four times, on average. Panel B: A Western blot of cell lysates isolated from HEK293T cells transiently transfect with constructs encoding GFP, spGFP∶Wnt1(209–239), and spGFP∶wnt1(209–239) N29D is shown. The blot was probed with anti-GFP antibodies.