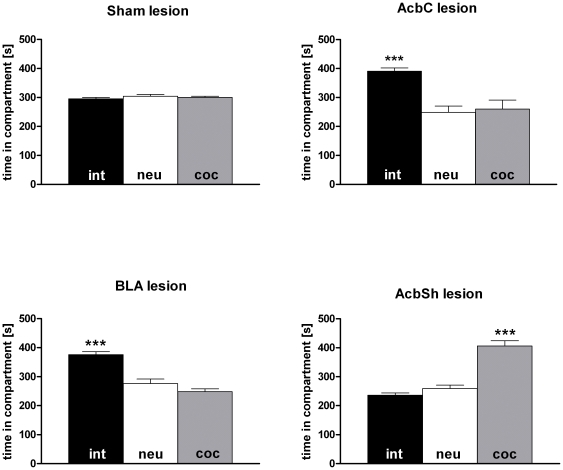
Figure 4. Lesions to nucleus accumbens core vs shell shifts preference for social interaction vs cocaine.
Shown are times spent in the stimulus-associated compartment during the CPP test (total 900 s) by rats that had undergone concurrent CPP training for social interaction (int) and cocaine (coc). Time spent in the neutral compartment of the 3-chamber CPP apparatus is designated “neu”. All times are presented as mean ± SEM. Before the concurrent CPP training, rats either received sham stereotaxic surgery including intracerebral injection of vehicle (sham lesion, n = 12) or received bilateral excitotoxic lesions of the AcbC (n = 6), the AcbSh (n = 6), or the BLA (n = 7). P values (ANOVA) for times spent in the respective chambers were P = 0.46 for the sham-treated rats, P = 0.0007 for the AcbC-lesion rats, P<0.0001 for the AcbSh-lesioned rats, and P<0.0001 for the BLA-lesioned animals. The two experimenters (MF and SK) were blind to the treatment.