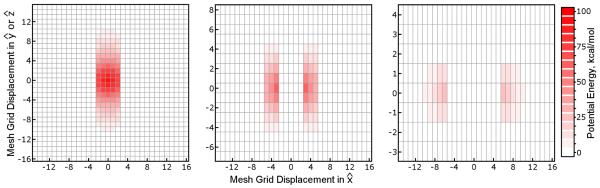
Figure 3. A three-level MLE scheme.
As illustrated above, the reciprocal space pair potential mesh can be split into three (or more) separate meshes, each with successively larger coarsening factors. Here, there are two coarsened meshes, with coarsening factors Cyz of 2 and 4, respectively. In this scheme, the pair potential in the lowest level mesh extends 2 pages; slabs of the lowest level charge mesh would require 4 pages of zero-padding. The pair potential in the intermediate level mesh has Tcut = 5, although only 6 of its pages have nonzero potential values in them (the thickness of the nonzero region of the mesh is 2 × 5 + 1 = 11 pages). While slabs of the intermediate-level charge mesh would require 10 pages of zero-padding, the intermediate level mesh is much smaller than the lowest level mesh, making such a degree of padding more economical. The color scale is not the same as that for Figure 1 because the SPME calculation this MLE scheme approximates was not the same; the diagram is intended for qualitative understanding only.