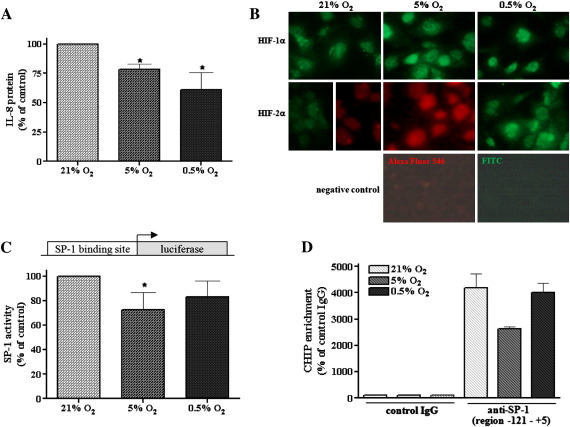
Fig. 5.
Effect of severe (0.5% O2) and mild (5% O2) hypoxia on IL-8 expression and SP-1 activity. (A) ELISA was done to assess the IL-8 protein level after 24 h of normoxia (21% O2) and mild (5% O2) and severe (0.5% O2) hypoxia. Note the decrease in IL-8 production under both conditions. (B) As shown by immunocytochemistry, both HIF subunits were activated in HMEC-1 cells under 0.5 and 5% O2; representative staining is shown (original magnification 100×). (C) Cells were cotransfected with pSP-1-luc vector containing the SP-1 binding site driving luciferase expression (500 ng) and a plasmid containing the LacZ gene (100 ng) as an internal control and after 24 h incubated under 21, 5, or 0.5% O2 for the next 24 h. Then the luciferase activity was measured. (D) ChIP assay was done to check the SP-1 binding to the IL-8 promoter under severe and mild hypoxia (6 h). Antibodies against IgG and SP-1 (anti-SP-1) were used. The SP-1 binding site within the IL-8 promoter was amplified using real-time reverse transcription–PCR as described under Materials and methods. Both SP-1 activity (C) and SP-1 binding to the IL-8 promoter (D) were slightly affected under both hypoxic conditions, but particularly under 5% O2. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of two to five independent experiments. *p < 0.05, comparing 21% vs 0.5 or 5% O2.