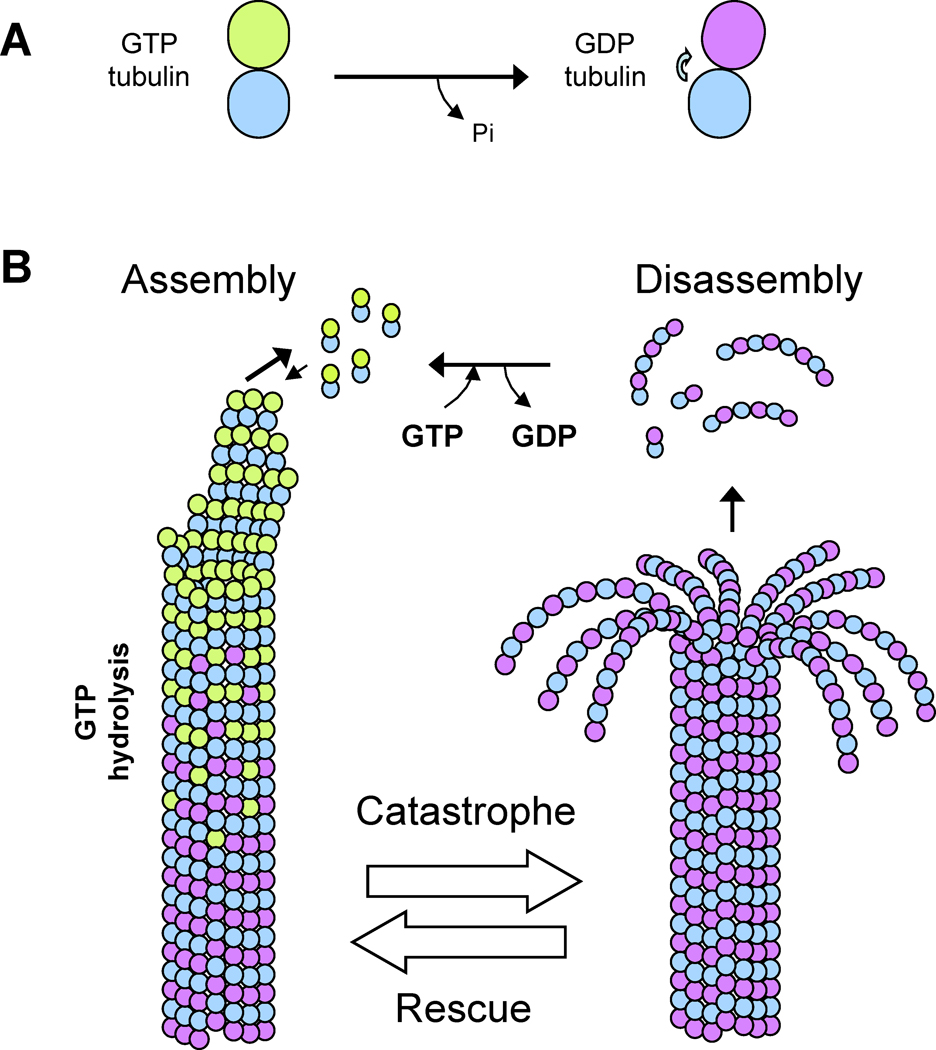
Figure 1. Assembly and disassembly of dynamic microtubules (MTs).
A) Conformational change of αβ-tubulin accompanying GTP hydrolysis. In the GTP state (in β-tubulin in green), α and β tubulin monomer interfaces result in “straight” tubulin dimer. In the GDP state αβ-tubulin dimer interface is curved by 5 degrees (arrow), leading to a “bent” tubulin dimer.
B) Structural changes at MT plus ends. During MT assembly, MT plus ends form a sheet-like group of straight protofilaments. GTP-tubulin dimers (green) assemble on the ends, forming a cap of GTP tubulin. GTP hydrolysis over time converts GTP-tubulin in the lattice to GDP-tubulin (note that the extent of the GTP cap is not known). In the MT disassembly phase, GDP-tubulin protofilaments curl and peel off the MT plus ends. The transitions between growth and shrinkage states are termed catastrophe and rescue.