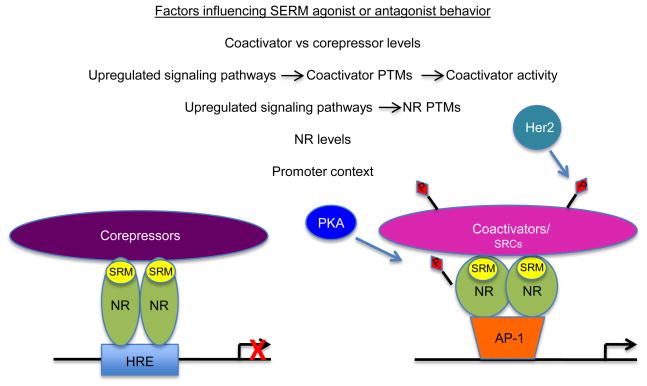
Figure 3. Multiple cellular factors influence coactivator-NR interactions in the presence of SRMs, affecting SRM functional effects on NR-mediated transcription.
Listed are several cellular variables, including NR and coactivator levels and activity, influenced by the differential upregulation of oncogenic signaling pathways, as well as gene-specific promoter contexts that determine whether a SRM will have agonist or antagonist effects. The cartoon demonstrates just some of these potential variables that can impact SRM antagonist/agonist activities and pathways that may be involved. Not all variable are likely to be in play at one time and are cancer, cell- and gene-dependent. SRM (selective receptor modulator); NR (nuclear receptor); HRE (hormone response element; AP-1 (activating protein 1); SRC (steroid receptor coactivator); PKA (protein kinase A); Her2 (human epidermal growth factor 2); P (phosphorylation).