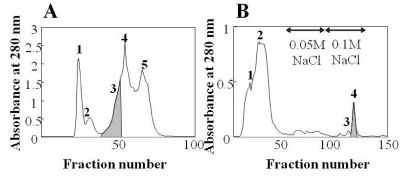
Figure 1.
Elution profiles for the isolation of aagardi toxin from H. t. aagardi venom. (A) The first step: H. t. aagardi crude venom (10 mg) was applied to a column of Sephadex G-50 (1.5 × 100 cm) equilibrated with 0.01 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8). The column was eluted with 0.01 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8). Fractions of 3.0 mL were collected at a flow rate of 13.5 mL/hr. (B) The second step: Peak 3 from the first step was applied to a column of CM52-cellulose (1.5 × 45 cm) equilibrated with 0.01 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8). The column was eluted with a step gradient of 0.01 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8) containing 0.05 M and 0.1 M NaCl. Fractions of 3.0 mL were collected at a flow rate of 13.5 mL/hr.