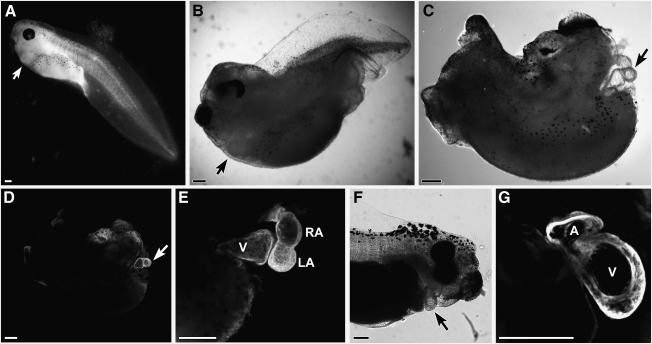
FIG. 5.
Ectopic activation of canonical WNT signaling in the early gastrula. This signaling pathway was promoted in the developing frog by treating stage 10.25 embryos with the GSK3 inhibitor SB415286. Types of malformations observed in responses to SB415286 treatment were embryos displaying: (A) mild defects consisting of a bent tail; (B) an anteriorized phenotype that results in a severely truncated tail, but fully developed head; and (C) a compound defect consisting of both a truncated tail and highly deformed head. Despite the differences in the severity of the defects, each of these embryos developed a functional and anatomically normal heart (arrows). Note that the ventral dermis overlaying the developing heart was removed from the latter embryo to better observe the organ's structure. (D) Same embryo as C, showing sarcomeric myosin immunolabeling of the heart (arrow). (E) High magnification of a heart from another SB415286-treated embryo that was incubated to stage 40. The sarcomeric myosin-immunolabeling highlights the developing ventricle (V), left (LA) and right atrium (RA) (F) SB415286-treated embryo that was incubated to stage 46 and exhibited an anatomically normal heart (arrow). (G) Same embryo at higher magnification, with sarcomeric myosin staining showcasing well-formed atrial and ventricular chambers. Scale bars=200 μm.