Figure 3. The Symmetry Breaking (SB) mechanism.
Top Panel The SB parameter, 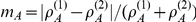 , is the normalized average difference of type-A molecule density around type-
, is the normalized average difference of type-A molecule density around type- region of polymers
region of polymers  and
and  . Its dynamics, from the initial symmetrical polymer looped state (as in the schematic picture in the Bottom Panel, “Stable Interaction”), is shown for two characteristic values of molecule homotypic interaction energy,
. Its dynamics, from the initial symmetrical polymer looped state (as in the schematic picture in the Bottom Panel, “Stable Interaction”), is shown for two characteristic values of molecule homotypic interaction energy, 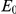 (here
(here 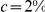 and
and 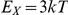 ). If
). If  ,
,  is close to zero: molecules are equally distributed around the polymers. If
is close to zero: molecules are equally distributed around the polymers. If 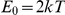 , after a transient of about ten hours,
, after a transient of about ten hours, 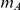 approaches one, i.e., either
approaches one, i.e., either  or
or  : molecules have aggregated around only one of the polymers, and their binding symmetry is broken (as in the schematic picture in the Bottom Panel, “Symmetry Breaking”). Bottom Panel The phase diagram in the
: molecules have aggregated around only one of the polymers, and their binding symmetry is broken (as in the schematic picture in the Bottom Panel, “Symmetry Breaking”). Bottom Panel The phase diagram in the  plane (for
plane (for  ) has three phases. If
) has three phases. If 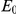 is below the transition line,
is below the transition line, 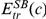 (red dashed line), the system is in one of its symmetric phases: the “Open State” phase (at low
(red dashed line), the system is in one of its symmetric phases: the “Open State” phase (at low  ) or the symmetrical “Stable Interaction” phase. If
) or the symmetrical “Stable Interaction” phase. If 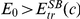 , the conformational symmetry is broken (“Symmetry Breaking” phase): the type-
, the conformational symmetry is broken (“Symmetry Breaking” phase): the type- loop persists only on one randomly chosen polymer, and type-
loop persists only on one randomly chosen polymer, and type- on the other.
on the other.

