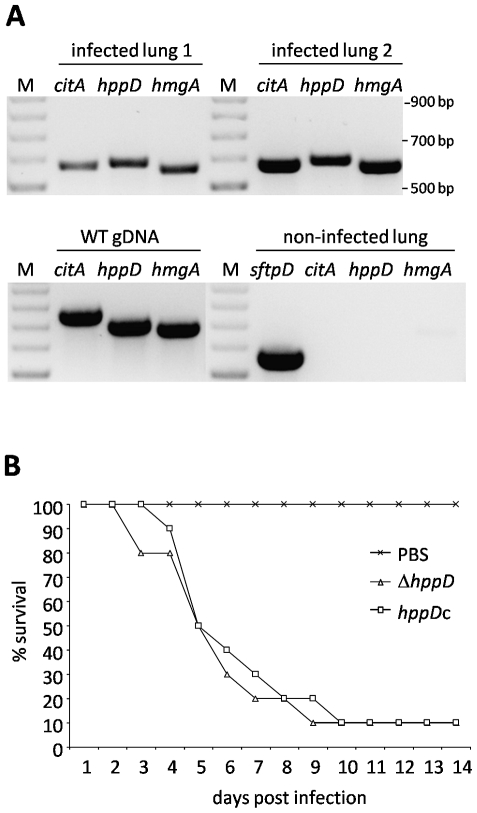
Figure 7. Role of tyrosine degradation and pyomelanin formation in pathogenicity.
(A) Transcription of hmgA and hppD in lungs of infected mice. Genomic DNA (gDNA) from A. fumigatus wild type was used as control. Two lungs isolated from immunosuppressed mice, which were intranasally infected with A. fumigatus conidia, provided material for cDNA synthesis. A noninfected (PBS) lung was used as control. Transcription of fungal genes was analyzed by reverse transcription-PCR. Transcription of A. fumigatus citA (citrate synthase) was used as control and transcripts of murine surfactant protein D (sftpD) ensured the quality of mouse cDNA. M denotes a 100 bp DNA ladder. (B) Virulence of strain ΔhppD in a murine infection model for invasive aspergillosis. Survival of corticosteroid-treated mice after intranasal infection with the ΔhppD mutant and the corresponding complemented strain hppDc was monitored over a period of 14 days. Infections were performed with a group of 10 mice for each strain tested.