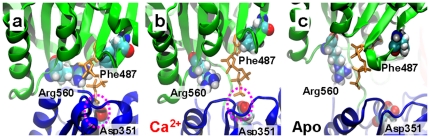
Figure 5. Active site geometry of SERCA in atomic detail.
(a) Crystal structure of SERCA bound to calcium and AMPPCP (orange sticks). Simulations at 500 ns of (b) Ca2+-bound and (c) Apo SERCA. In both cases, the predicted orientation of AMPPCP was obtained by using rigid-body docking simulations. Residues that are necessary for nucleotide binding (Phe487 and Arg560) and autophosphorylation (Asp351) are shown as van der Waals spheres. The N and P domains are rendered as green and blue ribbons, respectively. The dashed magenta ovals highlight the proximity between the γ-phosphate of AMPPCP and the carboxyl group of Asp351 in a and b, but not in c.