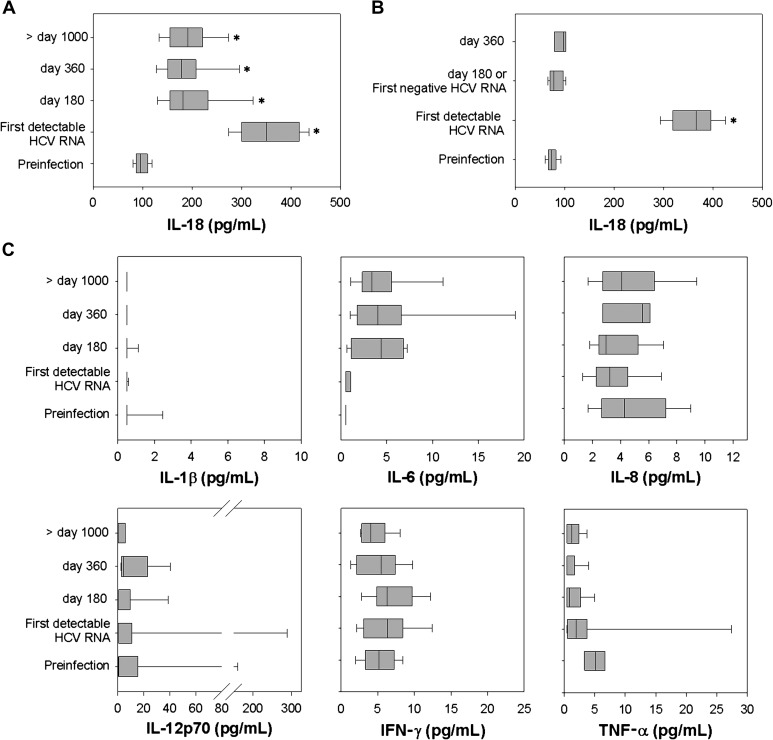
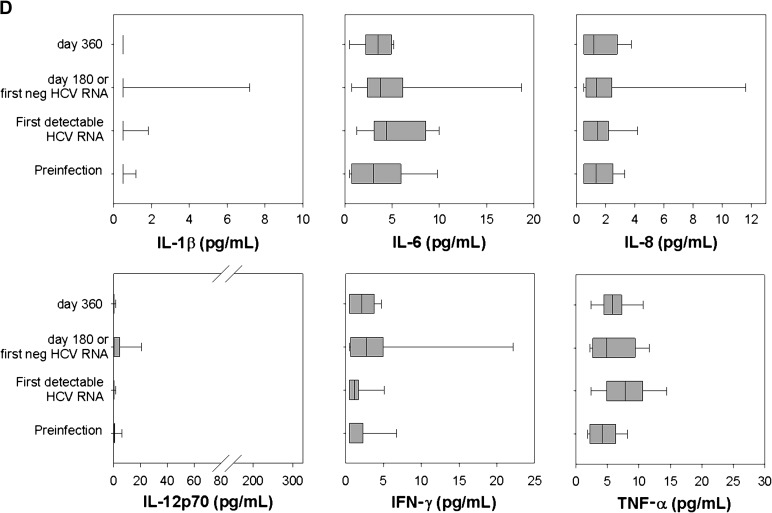
Figure 1.
Plasma interleukin (IL) 18 remains elevated in subjects with persistent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection but returns to baseline with clearance. Plasma IL-18 concentration (pg/mL) was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 25 subjects who developed persistent HCV infection (A) and 13 subjects who spontaneously cleared HCV infection (B). A, Plasma IL-18 concentration at a preinfection time point, on the day of first detectable HCV RNA, at approximately day 180 (range, 150–202), day 360 (range, 348–392), and a time point >1000 days of positive HCV RNA (range, 1078–1741). Median, upper, and lower quartile ranges are shown; (*) denotes P < .05 compared with preinfection level. B, Plasma IL-18 concentration at a preinfection time point, on the day of first detectable HCV RNA, and at the first day at which HCV RNA becomes undetectable (174 ± 86 days). Plasma IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12 p70, interferon (IFN)–γ, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–α concentrations (pg/mL) were measured at identical time points for subjects with persistent HCV infection (C) and subjects who spontaneously cleared HCV (D).