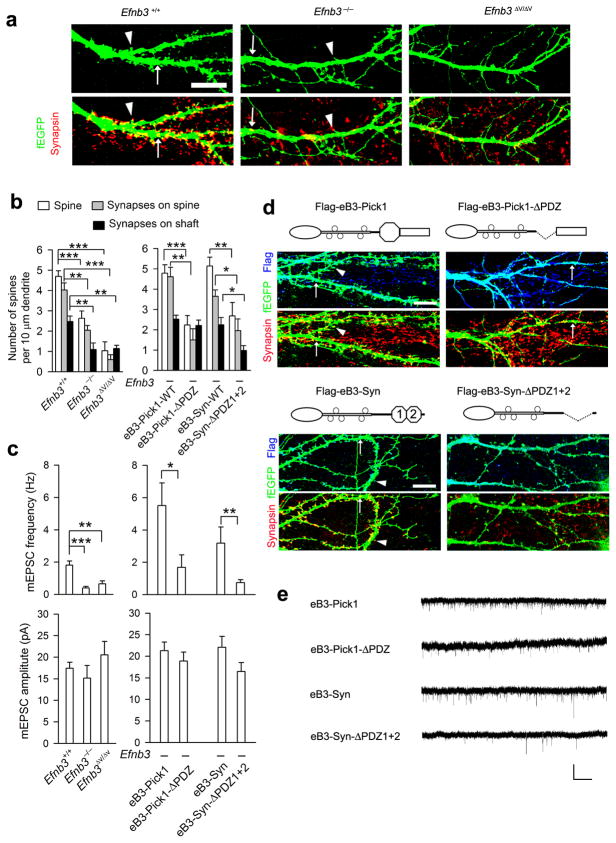
Figure 5. Pick1 and syntenin mediate ephrin-B3 reverse signaling through PDZ binding to control spine/synapse formation and synaptic function.
(a) Spine and synapse formation were indicated with a transfected f-EGFP reporter and presynaptic marker synapsin in 12d cultured hippocampal neurons from WT, Efnb3−/−, and Efnb3ΔV/ΔV mice. Arrowhead and arrow indicate synapse on spine and synapse on shaft, respectively. Scale bar: 10 μm. (b) The density of spines and synapses on spines (arrowhead)/shafts (arrow) were quantified. n = 10. (c) mEPSCs were recorded in 12–14 day cultured neurons from Efnb3 mutants and WT (left), and in Efnb3−/− hippocampal neurons that were infected with lentivirus packaged eB3-Pick1 or eB3-syntenin (Syn) expression vectors. Quantification of mEPSC frequency (upper) and amplitude (lower) is shown. n =15–20. Mean ± s.e.m. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 in b and c. (d) Expression of Flag-tagged WT eB3-Pick1 or eB3-syntenin (Syn) chimeric fusion proteins (left panels) in transfected Efnb3−/− neurons rescues spine and synapse formation as visualized with f-EGFP and synapsin in chimeric protein expressing neurons labeled with anti-Flag antibodies (upper panels). Expression of the eB3-Pick1-ΔPDZ or eB3-Syn-ΔPDZ1+2 fusion proteins deleted for the respective PDZ domains (right panels) had little if any effect on spine and synapse formation in Efnb3−/− neurons. Scale bar: 10 μm. (e) Example of mEPSC recorded in Efnb3−/− neurons expressing eB3-Pick1 or eB3-syntenin (Syn) fusion proteins and their PDZ deleted mutant forms. Scale bar: 40 pA (vertical) × 2 s (horizontal).