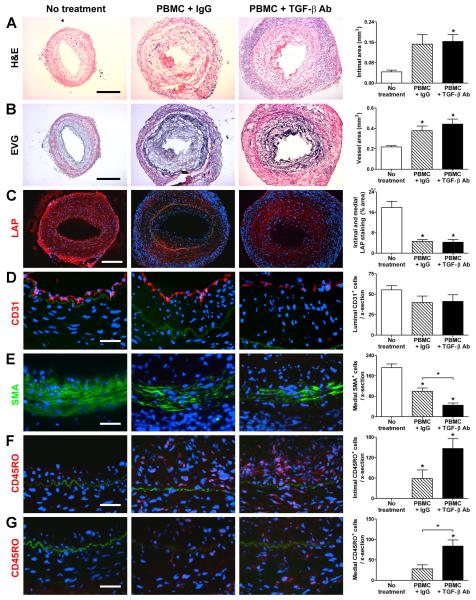
Figure 2. TGF-β inhibits medial infiltration and SMC loss in rejecting artery grafts.
Human coronary arteries were interposed into the aorta of SCID-beige mice that received an adoptive transfer of 0.5-3×108 allogeneic human PBMC (from one of 3 PBMC donors) at 1 wk post-op. The animals received no treatment (n=9 from 5 artery donors) or were treated with IgG (n=17 from 9 artery donors) or TGF-β antibody (n=17 from 9 artery donors) at 250 μg s.c., 3x per wk, from 1 to 5 wk post-op. Graft sections were stained with (A) H&E or (B) EVG at 5 wk post-op and representative photomicrographs are shown (bar, 300 μm). Intima and total vessel areas were calculated from EVG-stained graft sections. The artery grafts were also analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy using (C) PE-labeled anti-LAP (red color), (D) PE-labeled anti-CD31 (red color), (E) FITC-labeled anti-smooth muscle α-actin (SMA) (green color), and (F, G) PE-labeled anti-CD45RO (red color); the individual panels in (F) focus on the intima while those in (G) better illustrate the media. The internal elastic lamina is visible due to auto-fluorescence (green color). Representative photomicrographs are shown at lower magnification for LAP (bar, 200 μm) and at higher magnification (bar, 50 μm) for the cell lineage markers. The images were quantified as % positively-staining intima and media area for LAP or the number of CD31+ luminal cells, SMA+ medial cells, CD45RO+ intimal cells, and CD45RO+ medial cells were counted per cross (x)-section of grafts. *P<0.05, TGF-β Ab or IgG vs. No treatment,P<0.05, TGF-β Ab vs. IgG, one-way ANOVA.