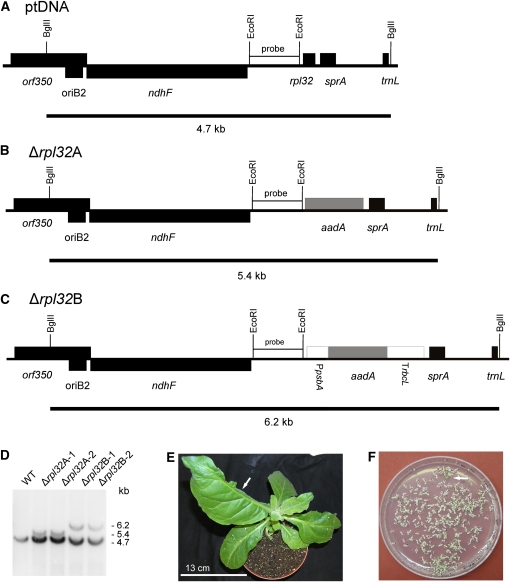
Figure 3.
Targeted Inactivation of the rpl32 Gene Encoding Plastid Ribosomal Protein L32.
(A) Physical map of the region in the tobacco plastid genome containing the rpl32 gene. Transcriptional orientations and labeling of restriction sites, hybridization probes, and hybridizing fragments are as in Figure 2.
(B) Map of the transformed plastid genome produced with plastid transformation vector pΔrpl32A. In this vector, the selectable marker gene aadA replaces the rpl32 gene and is driven by the native promoter upstream of rpl32.
(C) Map of the transformed plastid genome produced with plastid transformation vector pΔrpl32B. In this vector, a chimeric selectable marker gene cassette was used to replace the rpl32 gene. It consists of the promoter of the plastid psbA gene, the coding region of the aadA marker and the 3′ UTR derived from the rbcL gene.
(D) RFLP analysis of four plastid transformants. All lines are heteroplasmic and show the 4.7-kb wild type–specific hybridization band. The transplastomes give the expected 5.4-kb band (Δrpl32A) or 6.2-kb band (Δrpl32B). WT, wild type.
(E) Phenotype of a typical (heteroplasmic) Δrpl32 transplastomic plant. The arrow points to a misshapen leaf that lacks almost half of the leaf blade.
(F) Segregation of the rpl32 knockout allele in the progeny as determined by seed germination assays on synthetic medium containing spectinomycin. A single green antibiotic-resistant seedling (that still contains the transplastome) is marked by the arrow.
Bar in (E) = 13 cm.