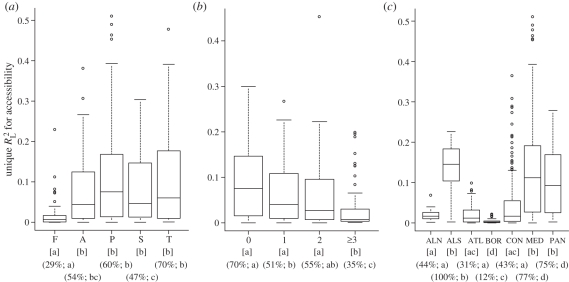
Figure 3.
Variation in species occurrences uniquely explained by accessibility for species with different (a) life forms (F, fern; A, annual herb; P, perennial herb; S, shrub; T, tree), n = 595; (b) long-distance dispersal (LDD) potential (measured as the number of LDD vectors), n = 346; and (c) climate-zone associations (ALN, northern-alpine; ALS, southern-alpine; ATL, Atlantic; BOR, boreal; CON, continental; MED, Mediterranean; PAN, Pannonian) n = 655 (shown for species with positive model-averaged accessibility coefficients, βMA(A)). In squared parentheses, identical letters indicate no significant difference between groups (p < 0.05; Mann–Whitney U-test, significance levels adjusted using Bonferroni correction). In round parentheses, percentage of all species in a given group with a positive βMA(A), and summed Akaike weights for accessibility of ≥95%; identical letters indicate no significant differences in percentages among groups (tested using χ2-tests, see the electronic supplementary material, appendix S4).