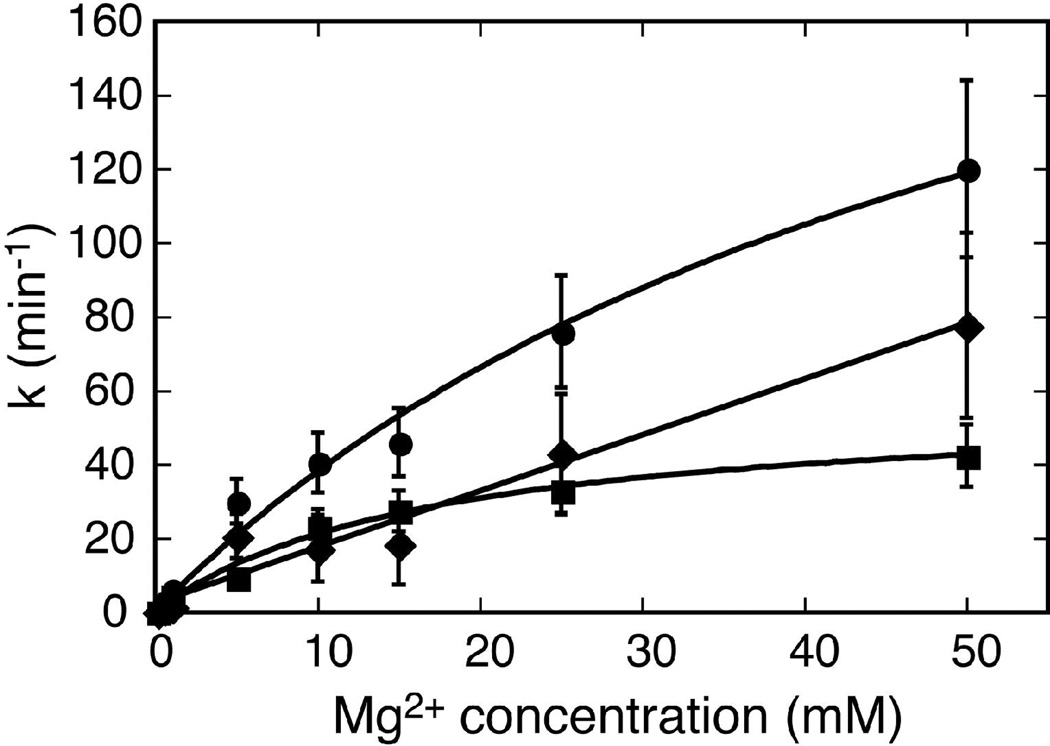
Figure 5.
Mg2+ dependence of the kinetics for the Schist26 and Schist21 constructs. A plot of kobs, cleave for Schist26 (circles), kcleave for Schist21 (squares), and calculated kligate (diamonds) vs. Mg2+ concentration. For kobs, cleave and kcleave the lines are fits of the Mg2+ dependence of the rate constant, k, to a two-state model for Mg2+ binding using the equation k = kmax [Mg2+]/([Mg2+] + [Mg2+]1/2), where kmax is the rate constant at saturating Mg2+, and [Mg2+]1/2 is the Mg2+ concentration required to achieve half the maximal cleavage rate constant. This analysis assumes a Hill coefficient of 1 since there was no evidence for cooperative binding of Mg2+ for any of the kinetic data. These fits yield [Mg2+]1/2 of 55 ± 10 mM for kobs, cleave for Schist26 and 17 ± 3 mM for kcleave for Schist21. The kligate does not saturate at the Mg2+ concentrations employed here making it impossible to determine a [Mg2+]1/2. Thus for kligate the solid line is a simple linear fit of kligate with [Mg2+]. The error bars are based on a 20% error between replicate experiments for the measured rate constants (see Table 1).