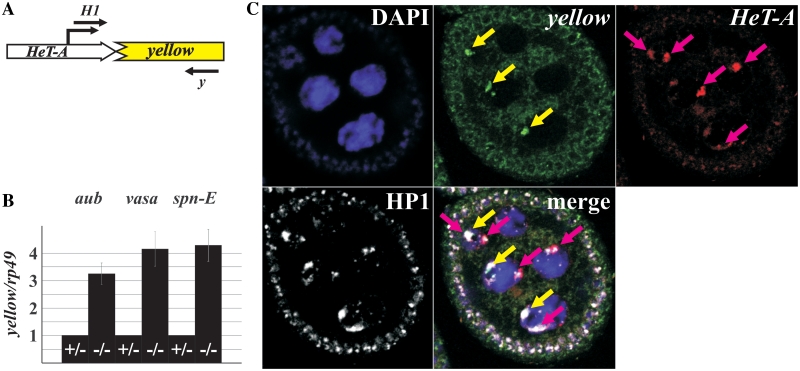
Figure 1.
HeT-A/yellow reporter gene expression in the piRNA pathway mutants. (A) A schematic representation of the HeT-A/yellow reporter construct. Position of the transcription start site is indicated by broken arrow. Primers used in the RT–PCR analysis are shown. (B) RT–qPCR analysis of the HeT-A/yellow transcript amount in the ovaries of spn-E, aub, and vasa mutants. Bars of histograms represent a ratio of HeT-A/yellow to rp49 transcript abundance in the ovaries of transheterozygous aubQC42/aubHN (–/–), spn-E1/spn-Ehls3987 (–/–), or vigEP812/vasPH165 (–/–) flies related to this ratio in aubQC42/CyO (+/−), spn-E1/TM3 (+/−), or vigEP812/CyO (+/−) females. (C) Terminally deleted chromosome recruits the telomere capping protein HP1 in ovaries. Immunostaining of HP1 (white) reveals numerous signals in the ovarian nuclei. DNA FISH was performed with yellow (green signals indicated by yellow arrows) or HeT-A (red signals indicated by pink arrows) DNA probes. HP1 locates at the ends of normal chromosomes (HeT-A staining) as well as of terminally deleted chromosome (yellow staining) of the z2 line. DNA is stained with DAPI (blue).