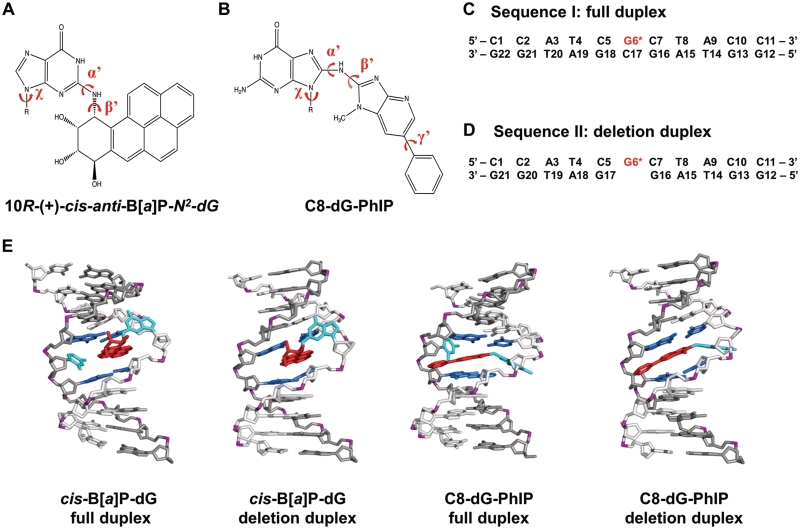
Figure 1.
Structures and sequences of cis-B[a]P-dG and C8-dG-PhIP-modified duplexes. (A) Chemical structure of the cis-B[a]P-dG adduct. The glycosidic torsion angle, χ for both modified duplexes is defined as O4′−C1′−N9−C4. The B[a]P-dG linkage site torsion angles, α′ and β′, are defined as follows: α′ = N1(G)−C2(G)−N2(G)−C10(B[a]P) and β′ = C2(G)−N2(G)−C10(B[a]P)−C9(B[a]P). (B) Chemical structure of the C8-dG-PhIP adduct. The PhIP-dG linkage site torsion angles, α′ and β′, are defined as follows: α′ = N9(G)−C8(G)−N(PhIP)−C2(PhIP) and β′ = C8(G)−N(PhIP)−C2(PhIP)−N1(PhIP). The torsion angle γ′ is defined as C7(PhIP)−C6(PhIP)−C1′(PhIP)−C2′(PhIP). (C) Sequence I. Sequence context of the 11/11-mer full duplex. (D) Sequence II. Sequence context of the 11/10-mer deletion duplex. G6*, colored in red, represents the lesion-modified guanine. (E) NMR solution structures for the cis-B[a]P-dG-modified 11/11mer full and 11/10mer deletion duplexes (34,35) and C8-dG-PhIP 11/11mer full duplex (33) utilized as initial structures for the MD simulations. The C8-dG-PhIP deletion duplex was modeled based on the cis-B[a]P-dG deletion duplex NMR structure (35), as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. The duplexes are viewed from the minor groove side. Hydrogen atoms and phosphate oxygen atoms are deleted for clarity. In the modified full duplexes, the lesion strand backbone is colored in light gray and the complementary strand is colored in dark gray. Phosphate atoms are colored purple. The adduct is colored red, the modified guanine and its partner base are colored cyan, and the neighboring bases are colored blue.