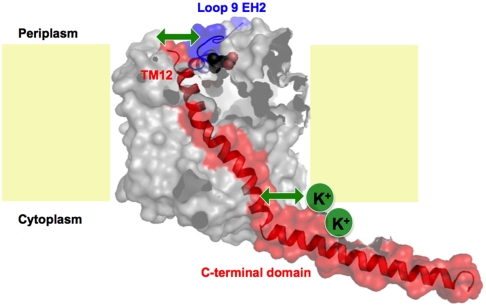
Fig. P1.
An extracellular K+-dependent interaction site modulates betaine binding of the transmembrane Na+-coupled betaine symporter BetP. In the Na+-coupled betaine symporter BetP (gray shaded molecule) from Corynebacterium glutamicum, the cytoplasmic K+-concentration establishes a second periplasmic substrate-binding (S2) site via an interaction (green upper arrow) between transmembrane helix 12 (TM12) and a helical segment (EH2) in loop9. This interaction is affected by K+ binding to the cytoplasmic side (green lower arrow) and the C-terminal domain. A betaine molecule (purple molecule at periplasmic side) is modeled in the X-ray structure of BetP (PDB entry code 2WIT) to indicate the location of this potential S2 site. The membrane bilayer is indicated yellow.