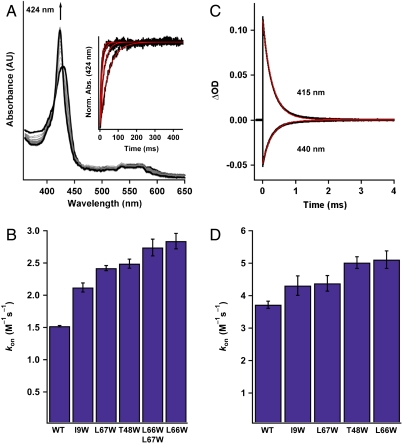
Fig. 4.
Determination of CO kon values (× 106 M-1 s-1) for the Ns H-NOX variants. (A) Time-resolved UV-visible spectra of CO binding to WT ferrous Ns H-NOX in a stopped-flow spectrometer (11.9 μM CO data is shown). (A, Inset) Single wavelength stopped-flow traces of the absorbance at 424 nm versus time for WT Ns H-NOX in the presence of varying CO concentrations. (B) Summary of CO kon values for the Ns H-NOX variants determined with stopped-flow spectroscopy (see Fig. S6 for a plot of kobs versus CO concentration). N = 3–5. Error represents the standard deviation. (C) Transient absorption traces of CO binding to WT ferrous Ns H-NOX under 1 atm of CO following laser photolysis. The trace at 440 nm represents the loss of the FeII-unligated species, and the trace at 415 nm represents the formation of the FeII–CO species. (D) Summary of CO kon values for all the Ns H-NOX variants determined with laser photolysis. N = 2. Error represents the standard deviation.