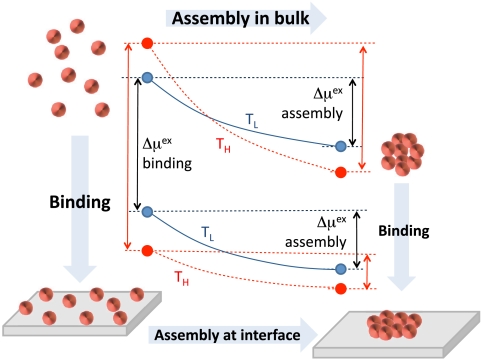
Fig. 4.
Schematic illustrating the thermodynamics of binding and assembly. The points represent free energies of solvating small objects individually (Left) and in the assembled state (Right), in bulk (Top) and at a hydrophobic interface (Bottom), at a lower (blue, TL) and a higher (red, TH) temperature near ambient conditions. Assembly: The driving force for assembly at hydrophobic interfaces is smaller than that in bulk, and is enthalpic, decreasing with increasing temperature, unlike in bulk. Binding: The driving force for binding small objects to a hydrophobic surface increases with temperature, so it is entropic, whereas for large objects, it is enthalpic.