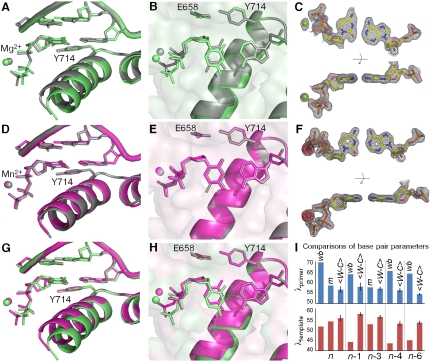
Fig. 3.
Comparison of C•A mismatch and T•A cognate base pairs placed at the polymerase insertion site. (A), (B) The C•A wobble (green) and T•A base (gray) pair obtained in the presence of Mg2+. For the C•A wobble pair, the O helix adopts the ajar conformation (A), the triphosphate is distorted, and the catalytic site is incompletely assembled (B). (D), (E) The C•A cognate shape (magenta) obtained in the presence of Mn2+. Comparison with a T•A base pair shows that the O helix is closed (D), the triphosphate is undistorted, and the active site fully assembled (E). (C), (F) Two views of composite omit maps of the C•A base pair (contoured at 1.2σ, C•A wobble; contoured at 2σ, C•A cognate) (green, Mg2+; purple, Mn2+). The presence of Mn2+ is confirmed by anomalous difference map (red, contoured at 4σ). (G), (H) Superposition of C•A wobble and C•A cognate at two different views showing the structural differences between the wobble and cognate conformations of this mismatch. (I) Variations of minor groove angles of C•A mismatch structures (wb, wobble; m, cognate mimic) or average cognate, Watson-Crick base-pair structures (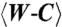 ) captured at five different positions. λprimer and λtemplate are defined as the angle between the glycosidic bond of primer or template nucleotide and a line between the C1′ atoms of the base pair. Complete tables of all nine base-pair parameters are included (Table S3). Analysis shown here is based on molecule 1 of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit; molecule 2 is described in Table S3. The capture of a nucleotide at the insertion site involves the use of dideoxy analogs (34). Additional structures were determined with a 2′-deoxycytidine triphosphate which confirms the results described here (Fig. S1).
) captured at five different positions. λprimer and λtemplate are defined as the angle between the glycosidic bond of primer or template nucleotide and a line between the C1′ atoms of the base pair. Complete tables of all nine base-pair parameters are included (Table S3). Analysis shown here is based on molecule 1 of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit; molecule 2 is described in Table S3. The capture of a nucleotide at the insertion site involves the use of dideoxy analogs (34). Additional structures were determined with a 2′-deoxycytidine triphosphate which confirms the results described here (Fig. S1).