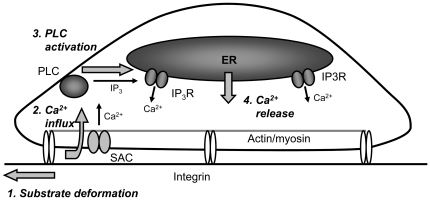
Figure 6. Schematic diagram depicting the hypothesized mechanism of calcium response upon mechanical vibration stimulation.
The substrate gel deformation causes a calcium influx through the membrane stretch-activated channels (SAC), activating phospholipase C (PLC). PLC then produces IP3 and calcium is subsequently release from intracellular stores (ER) due to IP3 signaling (through IP3 receptors, IP3R).