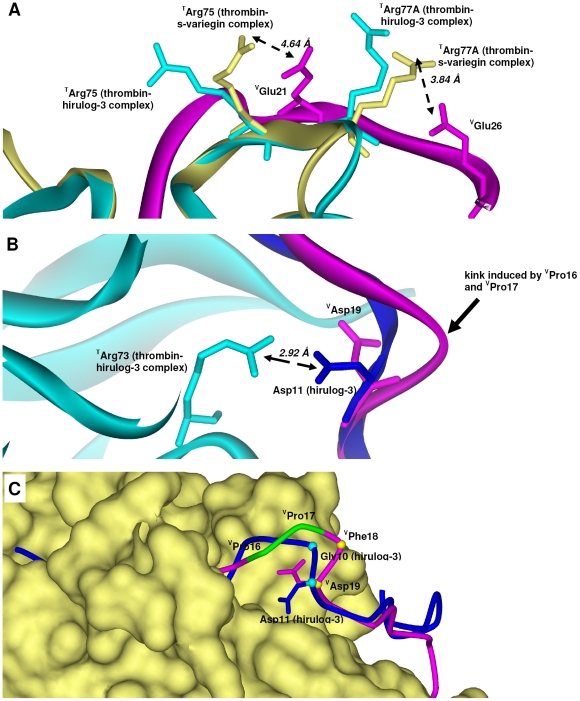
Figure 4. Electrostatic interactions in thrombin:s-variegin structure.
(A) s-Variegin and hirulog-3 have distinct ion pairs formed with exosite-I of thrombin despite high sequence identity. A salt bridge (3.84 Å) between VGlu26 (pink) and TArg77A (yellow) is absent in hirulog-3 as TArg77A (cyan) points away from the inhibitor. Weak salt bridge (4.64 Å) is also likely between VGlu21 (pink) and TArg75 (yellow) rotated 90.5° about Cβ compared to TArg75 in hirulog-3 bound thrombin (cyan) to facilitate interaction with VGlu21 (pink). Electron density maps of residues involved are shown in Figure S2A. (B) The strong ion pair (Asp11∶TArg73, 2.92 Å) in thrombin:hirulog-3 structure is absent in thrombin:s-variegin structure since VAsp19 (pink) pointed to an opposite direction compared to the analogous hirulog-3 Asp11 (blue) due to a kink in s-variegin backbone (pink). Electron density maps of residues involved are shown in Figure S2B. (C) The presence of a VPro16-VPro17 (green) in s-variegin resulted in the kink. Superimposition of s-variegin (pink, only Cα positions traced) and hirulog-3 (blue, only Cα positions traced) based on their thrombin structures showed displacement of VPhe18 and VAsp19 from their corresponding residues Gly10 and Asp11 of hirulog-3 by 3.11 Å and 0.79 Å (measured by Cα positions), respectively. As a result, the distance between TArg73 and VAsp19 charges are 5.83 Å, rendering electrostatic interactions impossible.