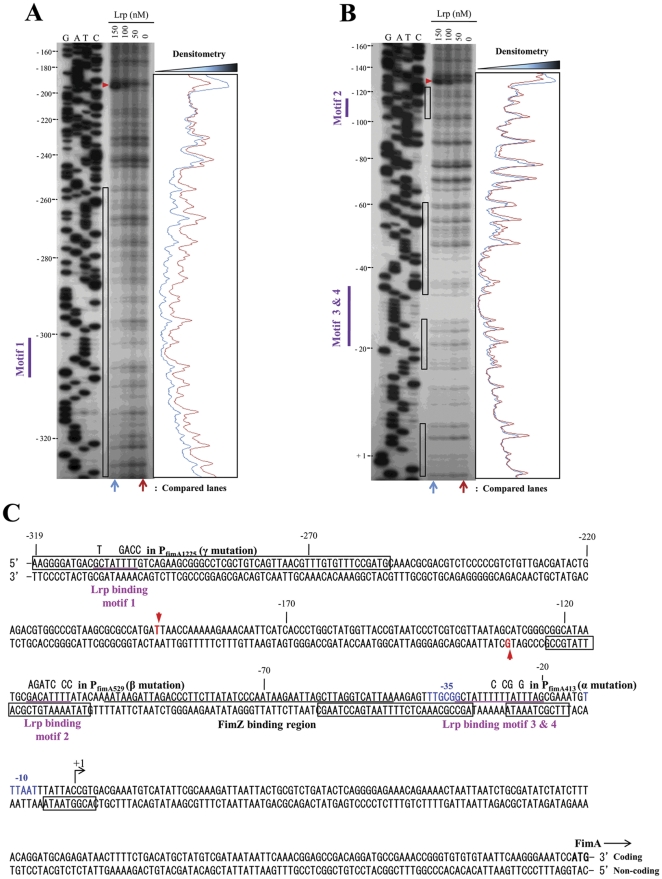
Figure 3. DNase I footprinting of Lrp binding to the PfimA region.
Both coding (A) and noncoding (B) strands were subjected to the DNase I protection assay. These strands were 32P-labeled at 5′ ends as described in Materials and Methods. Lrp was added at 150, 100, 50, and 0 nM. The DNase I protection products were separated in a sequencing gel next to the corresponding DNA sequencing products (lanes G, A, T, and C). The results from panels A and B are summarized in panel C. The coordinates in the panels A, B, and C are numbered with respect to the fimA transcription start site (+1) [15]. The black open boxes indicate DNA bases that were protected from DNase I digestion by Lrp. Hypersensitive bases are indicated with red arrowheads. The putative Lrp-binding motifs are shown as purple bars on the left side of the gels, and are underlined (purple) in panel C. Base changes in the site-directed mutations of the Lrp-binding motifs are shown over the wild-type bases. The FimZ-binding region [15] is also underlined (black). The putative −35 and −10 consensus sequences for RNA polymerase are shown in blue letters. The translation start codon (ATG) for the fimA gene is shown in bold letters. Arrows indicate orientation of transcription or translation.