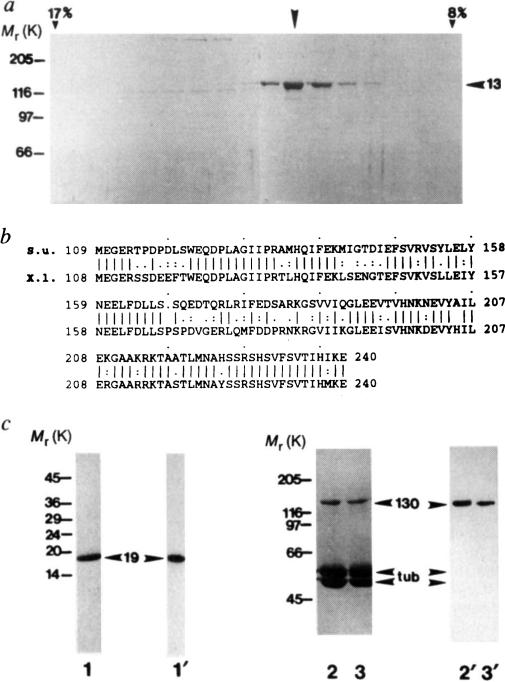
FIG. 1.
Purification of KRP130 and corresponding motor-domain antibodies for electron microscopy, a, SDS-polyacrylamide gel of fractions from sucrose density gradient centrifugation of KRP130 (ref. 13). Arrowhead indicates peak fraction. Percentage sucrose (w/v) is indicated for two fractions, b, Best-fit comparison of the sea urchin (S.u.) Eg5-related motor-domain subfragment used for raising Eg5 motor-domain antibodies, and the corresponding region of Xenopus laevis (X.I.) Eg5 (identity 69%, similarity 83%). c, Characterization of the Eg5 motor-domain antibody. SDS-polyacrylamide gels (1–3) and corresponding anti-Eg5 motor-domain immunoblots (1′–3′) of a purified fusion protein of Mr 19K, (His)6-SU Eg5 motor, comprising the sea-urchin Eg5-related motor-domain fragment fused to a polyhistidine tag (1,1′), and KRP130 pelleted with MTs in the presence of the nonhydrolysable ATP analogue, 5′adenylyl-β,γ-imidodiphosphate (AMP–PNP) (2,2′) or ATP (3,3′) in low salt. Numbers on the left refer to Mr of standards. Arrowheads indicate recombinant motor-domain fragment (19), tubulin (tub) and KRP130 (130).
METHODS KRP130 was purified from Drosophila melanogaster embryos13 and rotary-shadowed directly or following co-pelleting with MTs in AMP–PNP or ATP (KRP130 binding to MTs is ATP-sensitive at high but not low ionic strength; Fig. 1c and ref. 13). Antibody specific for KRP130 motor domains (Figs 1c and 4a) was raised against a recombinant motor-domain fragment of a sea-urchin egg protein, KRP170, that is a close relative of frog Eg5. Expression of a KRP170 motor-domain fragment complementary DNA in pRSETB vector yielded a (His)6-SU Eg5 motor fusion protein of Mr 19K, which was purified by Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid metal-chelate affinity chromatography followed by SDS-PAGE electroelution (Fig. 1c, lane 1) and used to raise rabbit polyclonal antibody. Specific antibody was affinity purified from serum using the 19K fusion protein coupled to agarose, analysed by immunoblotting (Fig. lc) and used for electron microscopy (Fig. 4a).