Figure 3.
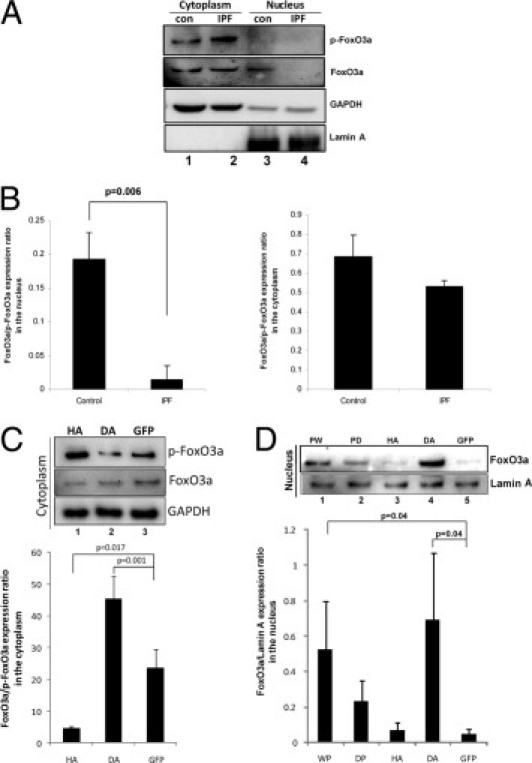
Nuclear FoxO3a levels are low in IPF fibroblasts. A: Serum-starved control (con) and IPF fibroblasts were cultured on polymerized collagen for 24 hours. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were collected, and p-FoxO3a and FoxO3a levels were measured by Western blot analysis. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a cytoplasmic loading control. Lamin A was used as a nuclear loading control. B: The FoxO3a/p-FoxO3a expression ratio in the nucleus (left) or cytoplasm (right) was quantified in control and IPF fibroblasts cultured on polymerized collagen by densitometry. C: Top: IPF fibroblasts infected with an adenovirus expressing HA, DA, or empty vector (GFP) were cultured on polymerized collagen for 24 hours, and the cytoplasmic fraction was separated. Western blot analysis was performed to measure p-FoxO3a and FoxO3a protein levels. GAPDH was used as a loading control for the cytoplasmic fraction. Bottom: The FoxO3a/p-FoxO3a expression ratio was quantified by densitometry. D: Top: IPF fibroblasts infected with an adenovirus expressing PW, PD, HA, DA, or empty vector (GFP) were cultured on polymerized collagen for 24 hours, and the nuclear fraction was separated. Western blot analysis was then performed to measure FoxO3a protein levels. Lamin A was used as a nuclear loading control. Bottom: Densitometric analysis of the FoxO3a/p-FoxO3a expression ratio in the nucleus.
