Figure 6.
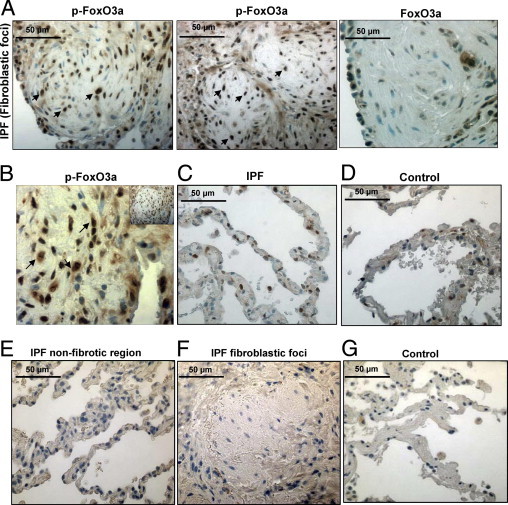
Cells within IPF fibroblastic foci are immunoreactive for inactive FoxO3a. IHC was performed on lung tissue from patients with IPF or patients with histologically normal lungs (n = 3 for both) using an anti-p-FoxO3a antibody. The specimens were counterstained with hematoxylin. A: Left and middle: Representative p-FoxO3a staining of a fibroblastic focus in IPF patient tissue is shown. Original magnification, ×40. Many cells in the fibroblastic focus display strong immunoreactivity for p-FoxO3a (arrows). Right: Representative FoxO3a staining of a fibroblastic focus in IPF patient tissue is shown. Original magnification, ×40. B: Increased magnification of a ×40 image shown as an insert to illustrate nuclear and cytoplasmic staining of p-FoxO3a in the fibroblastic focus (arrows). C: Representative p-FoxO3a staining of the nonfibroblastic foci area of IPF patient tissue is shown. Original magnification, ×40. The number of cells immunoreactive for p-FoxO3a is relatively low compared with that of cells in fibroblastic foci in A. D: A nonfibrotic lung control specimen stained for p-FoxO3a using 3,3-diaminobenzidine substrate. Original magnification, ×40. E–G: Nonfibrotic region (E) and fibroblastic foci (F) of IPF tissue and alveoli of control lung tissue (G) were stained with secondary antibody only (negative control). Original magnification, ×40.
