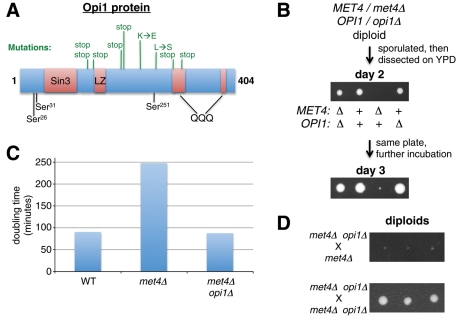
FIGURE 3:
Opi1p is required for the slow growth of met4Δ cells. (A) The mutations in the OPI1 gene are depicted in relation to the encoded Opi1p protein and its previously determined domains (Sreenivas and Carman, 2003). The following structural and functional domains are depicted: Sin3 (Sin3-interacting), LZ (leucine zipper), and QQQ (glutamine rich). Protein kinase A phosphorylates residues Ser-31 and Ser-251, whereas protein kinase C phosphorylates Ser-26. (B) Deletion of OPI1 causes a met4Δ haploid to grow like wild type. A met4Δ/MET4 opi1Δ/OPI1 diploid (DBY12225) was sporulated, and the resulting tetrads were dissected on YPD plates. The tetrads showed the 2:2, 3:1, and 4:0 large:small patterns as expected. The met4Δ opi1Δ cells remained methionine auxotrophs. (C) The doubling time of met4Δ is higher than that for MET4 or met4Δ opi1Δ. The MET4 (DBY12000), met4Δ (DBY12214), and met4Δ opi1Δ (DBY12226) strains were inoculated into YPD at low density and the cell concentration was followed until they reached saturation. The exponential phase of growth was used to calculate the doubling time only for cultures that did not develop growth suppression. A representative graph from many experiments is shown. (D) The opi1Δ allele acts recessively to suppress the growth defect of a met4Δ strain. Top, a met4Δ haploid (DBY12214) was crossed to a met4Δ opi1Δ haploid (DBY12227), and the resulting met4Δ/met4Δ opi1Δ/OPI1 diploids (three are shown) were grown for 2 d. Bottom, a met4Δ opi1Δ haploid (DBY12227) was crossed to a met4Δ opi1Δ haploid (DBY12226), and the resulting met4Δ/met4Δ opi1Δ/opi1Δ diploids (three are shown) were grown for 2 d.