Figure 4.
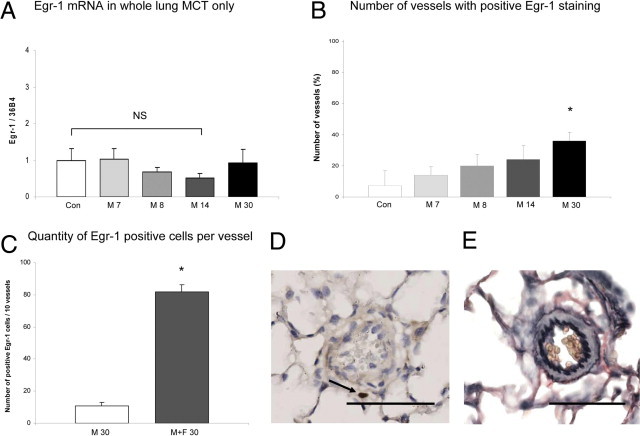
Egr-1 expression during pulmonary vascular remodeling in non-neointimal PH. To further emphasize the relationship among increased flow, Egr-1 up-regulation, and neointimal development, we investigated Egr-1 expression in a non-flow, non-neointmal PAH model (monocrotaline-only rats). See detailed description in Materials and Methods. A: Egr-1 expression relative to 36B4 per experimental group in whole lung. Bars indicate mRNA increase compared with controls. Expression levels in the control group are set to 1. Egr-1 mRNA expression is not up-regulated in whole lung in monocrotaline-induced vascular remodeling. B: Percentage of intra-acinar vessels staining positive for Egr-1 per experimental group. The number of vessels that show positive Egr-1 staining is increased in the M 30 group (*P < 0.05 versus controls). However, this number is far less compared with the number of vessels in the M+F 30 group as seen in Figure 3A. Also the number of positive Egr-1 cells per vessel in the end-stage groups differ (C). In addition, localization of Egr-1 staining differed in the M 30 group compared with M+F 30 group as seen in D. Typical example (original magnification, ×400) of Egr-1 staining in the M 30 group where Egr-1 staining was mainly found perivascularly. E: Typical example (original magnification, ×400) a Verhoeff staining of a peri-acinar vessel with media hypertrophy seen in the M 30 group. Administration of monocrotaline only never resulted in neointimal formation at M 30. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus controls. CON, pooled sham groups Scale bar = 50 μm.
