Figure 10.
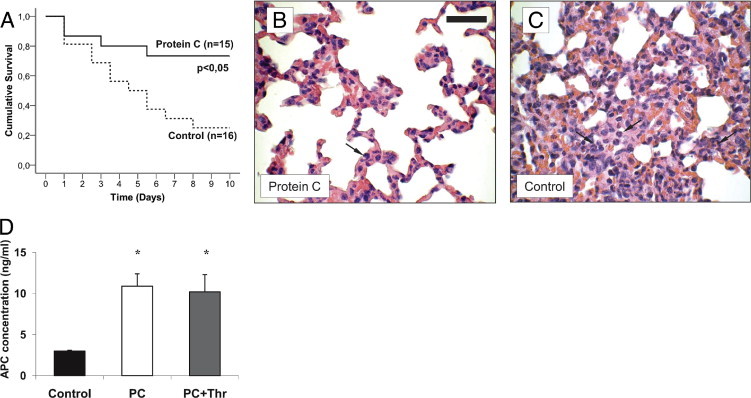
Protein C (PC) treatment during lethal endotoxemia. Lethal endotoxemia was induced by Escherichia coli LPS (40 mg/kg i.p.) and treated by i.v. of 100 U/kg PC or control solution at 30 minutes, and at 8 and 24 hours after LPS challenge. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis is shown for PC treated (n = 15) and control (n = 16) mice (A). Lungs of PC treated (B) and control mice (C) were harvested at the second day after LPS challenge and prepared as 3-μm paraffin-embedded sections for H&E staining. Micrographs are representative for at least three mice per group. Arrows indicate infiltrating neutrophils. Reference bar for (B) and (C) is shown in (B) and represents 50 μm. Plasma concentrations of human activated protein C (APC) (ng/mL) were measured at approximately 24 hours after LPS injection in PC-treated and control mice (D). Some PC-treated mice were additionally administered human α-thrombin-boostered PC activation and served as positive controls (PC+Thr). All values are presented as mean ± SEM from at least four mice per group. Significant differences (*P < 0.05) to control mice are indicated.
