Figure 3.
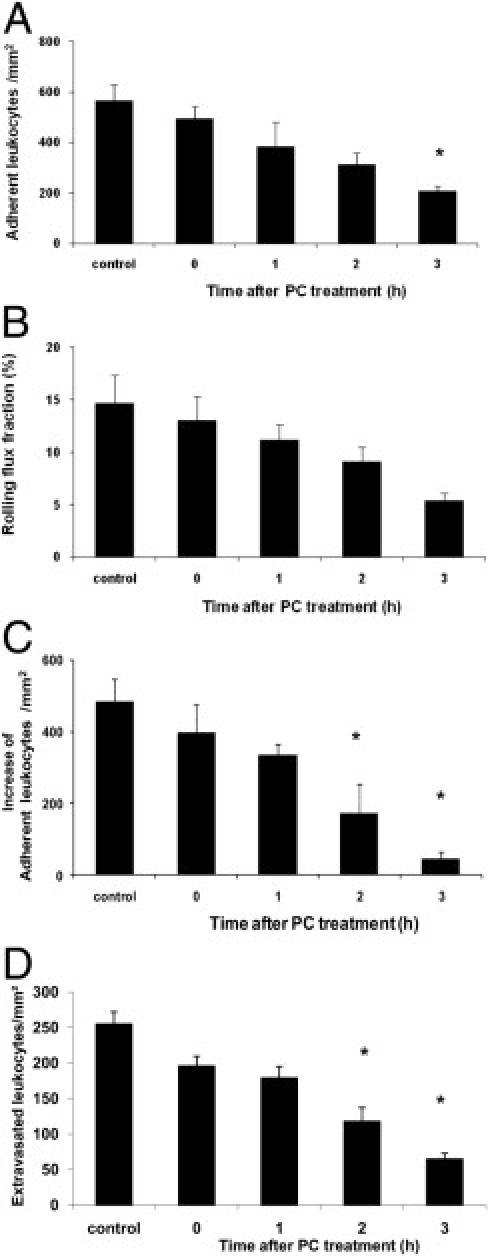
Leukocyte recruitment in trauma-induced inflammation after protein C (PC) treatment. Leukocyte adhesion (per mm2 of surface area) and rolling flux fraction (RFF) (percentage) after trauma-induced inflammation were observed in mice treated with 100 U/kg PC at different time points before microscopic observation and in control mice, which received isotonic human serum albumin (8 mg/mL) for 3 hours. First, the number of adherent leukocytes (A) RFF (B) in surgically prepared cremaster muscle venules were analyzed under baseline conditions. Next, the additional increase of leukocyte adhesion over baseline (per mm2 of surface area) is shown 3 minutes after systemic administration of 600 ng of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 for the respective PC treatment intervals and control condition (C). Leukocyte transmigration (D) was observed in Giemsa-stained cremaster muscle whole mounts obtained after the respective intravital microscopic experiments. All values are presented as mean ± SEM from three or more mice per group. Significant differences (*P < 0.05) to control are indicated.
