Figure 4.
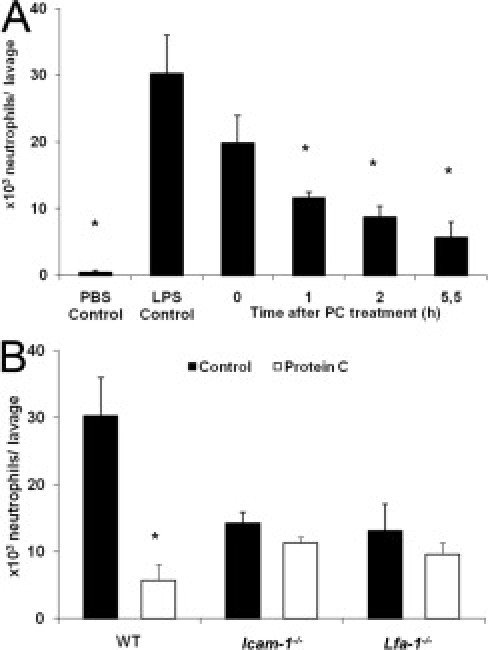
Impact of protein C (PC) on leukocyte emigration into the bronchoalveolar space in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced acute lung injury (ALI). In a 6-hour model of LPS-induced ALI, the number of intra-alveolar neutrophils, obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage were analyzed in wild-type (WT) mice treated with 100 U/kg PC at different time points and compared to WT control mice (A). Time between PC treatment and bronchoalveolar lavage is referred to as “Time after PC treatment”. PBS control mice were injected with PBS instead of LPS. In parallel, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (Icam-1)−/− and lymphocyte function assiciated antigen-1 (Lfa-1)−/− mice were treated with 100 U/kg PC 30 minutes after LPS application and were compared to untreated control mice and respective WT mice (B). All values are presented as mean ± SEM from at least three mice per group. Significant differences (*P < 0.05) to LPS control mice are indicated.
