Figure 6.
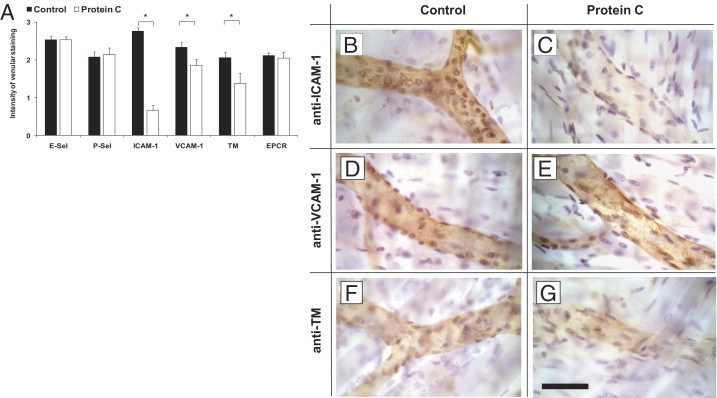
Expression of P- and E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), thrombomodulin (TM), and endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) in tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-stimulated cremaster muscles. Immunohistochemistry was performed to assess endothelial expression of P-selectin, E-selectin, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, TM, and EPCR in TNF-α-stimulated cremaster muscle venules for protein C (PC) (100 U/kg) treated or control mice (at least three mice per group). For P-selectin (P-Sel), E-selectin (E-Sel), ICAM-1, and VCAM, primary antibodies were injected systemically and incubated for 10 minutes. Cremaster muscle whole mounts were then fixed and permeabilized. Antibodies against TM and EPCR were administered after permeabilization. Biotinylated secondary antibody, peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin, and diaminobenzidine (DAB) were used to detect endothelial expression as brown signal. Counterstaining was performed by H&E. The intensity of venular immunostaining was analyzed semi-quantitatively and presented as the mean ± SEM for all antibodies in PC-treated mice and compared to respective control mice (A) 0 = no, 1 = weak, 2 = medium, 3 = strong signal. Significant differences (*P < 0.05) to the control are indicated. Representative micrographs are depicted to illustrate the endothelial expression of ICAM-1 (B), VCAM-1, (D) and TM, (F) in control and PC-treated mice (C, E, G, respectively). Scale bar for (B–G) is shown in G and represents 50 μm.
