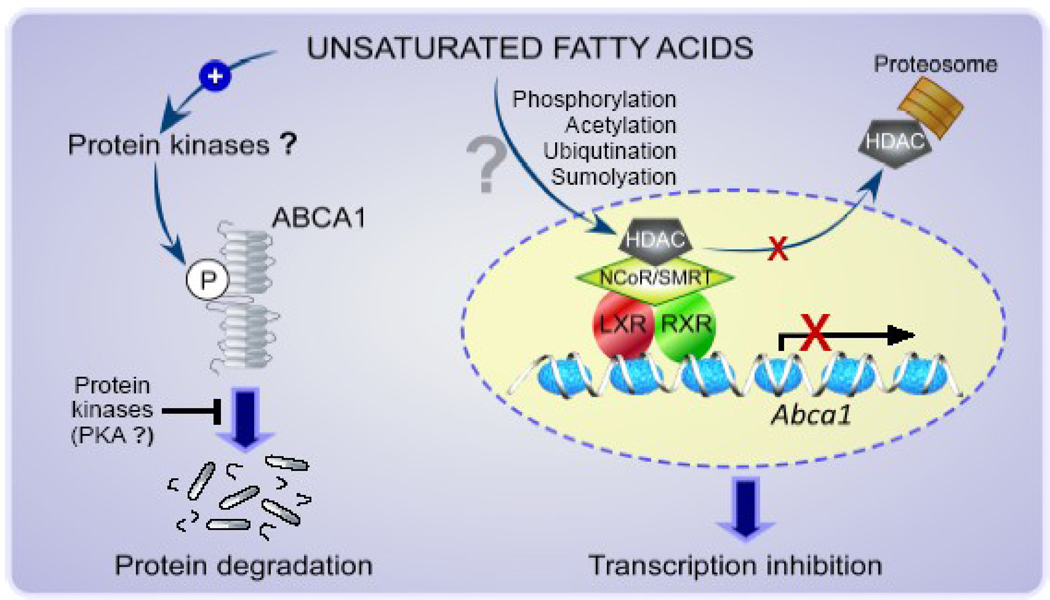
Figure 2. Hypothetical mechanisms for the regulation of ABCA1 expression by unsaturated fatty acids.
Post-transcriptional regulation of ABCA1 by unsaturated fatty acids may also occur via mechanisms involving protein kinases that phosphorylate (P) ABCA1 to facilitate the protein degradation. In contrast, other types of kinases such as PKA may inhibit the action of unsaturated fatty acids and stabilize the protein. Unsaturated fatty acids may also repress ABCA1 transcription in a LXR-dependent manner. Activity or recruitment of an HDAC as a component of NCoR/SMRT coprepressor complex that is associated with a LXR/RXR heterodimer in the promoter of Abca1 may be altered by unsaturated fatty acids via post transcriptional histone modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiqutination and sumolyation.