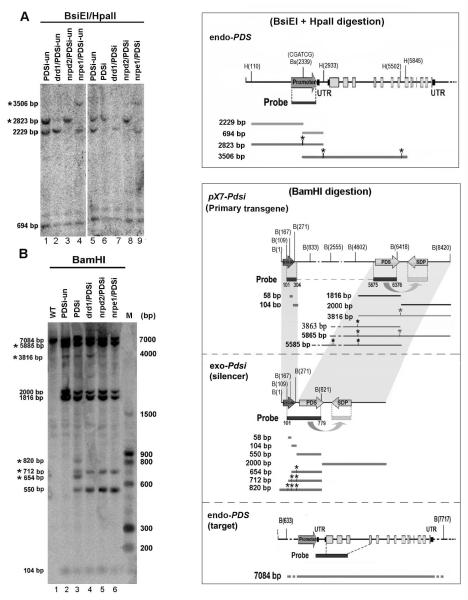
Figure 6. Analysis of DNA methylation of the endo PDS gene and the exo-Pdsi silencer.
(A) Detailed analysis of methylation in endo-PDS promoter using two methylation-sensitive enzymes BsiEI and HpaII sites. DNA was isolated from leaf samples of each genotype with or without inducer treatment and digested with BsiEI and HpaII. DNA gel blots were analyzed with a 32P-labeled promoter DNA probe. PDSi, with inducer; PDSi-un, without inducer. BsiEI and HpaII sites along the endo-PDS genome are shown in the upper right rectangle. Sizes of DNA fragments resulting from complete and methylation-resistant digestion (labeled with *) that could be detected with the promoter probe are shown in the box on the right panel. These DNA fragments are indicated on the left of the gel. (B) Detailed analysis of methylation in primary pX7-Pdsi, exo-Pdsi and endo-PDS using methylation-sensitive enzymes BamHI sites. DNA samples and blotting were as described in (A), except digestion with BamHI. BamHI sites along each construct are shown in the box on the right. DNA probe covered both the G10-90 promoter and the Pds fragment is indicated under each construct. Sizes of DNA fragments resulting from complete and methylation-resistant digestion (*) that could be detected with the DNA probe are shown in the box. These DNA fragment are also marked on the left of gel. The positions of labeled marker DNA fragments are shown on the right.