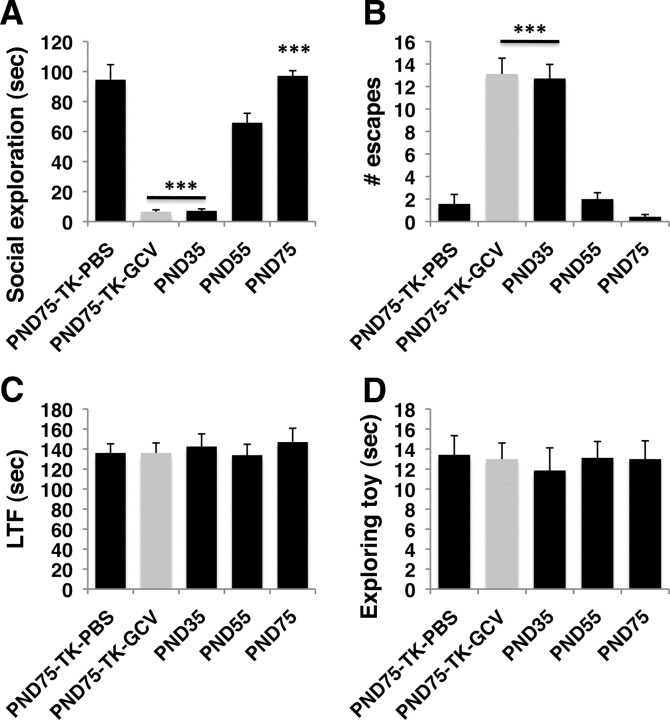
Figure 7.
Juvenile neurogenesis is required to support the increase in socialization seen during this period. TK-GFP females were exposed to either intracerebroventricular PBS or GCV (n = 8–7 for each condition), singly housed, and tested in affiliative behavior on PND 75 (PND75-TK-PBS or PND75-TK-GCV). BALB/cByj wild-type females were singly housed on PND 27 and tested in the affiliative assay on either PND 35 (n = 7), PND55 (n = 8), or PND 75 (n = 7). Note that these mice were not exposed to surgery. A, Social exploration increased with age. B, Number of escapes decreased with age. Note that juvenile neurogenesis was intact in all groups except for the PND75-TK-GCV group (gray) and that social behavior of PND75-TK-GCV resembles that of PND 35 mice. C, Latency to find food (LTF). D, Time spent exploring inanimate object. ***p < 0.0005 compared with PND 55 group mice using Tukey-HSD post hoc analysis following one-way ANOVA.