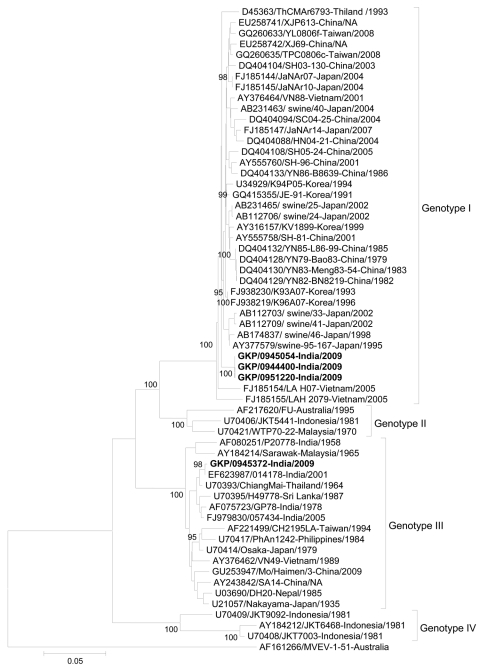
Figure.
Phylogenetic tree constructed by using a 1,381-nt Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) envelope sequence directly amplified from cerebrospinal fluid specimens collected during the acute phase of illness from hospitalized acute encephalitis syndrome patients, India, September–November 2009. Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis were conducted by using ClustalW software (www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/index.html) and MEGA version 4 (www.megasoftware.net). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method and the maximum composite likelihood model. The robustness of branching patterns was tested by 1,000 bootstrap pseudo replications. Sequences obtained in this study are indicated in boldface. Genotypes are indicated on the right. Viruses were identified by using the nomenclature of accession number–strain name–country of origin/year of isolation. Bootstrap values are indicated above the major branch. The tree was rooted within the Japanese encephalitis serogoup by using Murray Valley encephalitis virus (AF161266) and 55 JEV sequences from GenBank were used in the analysis. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.