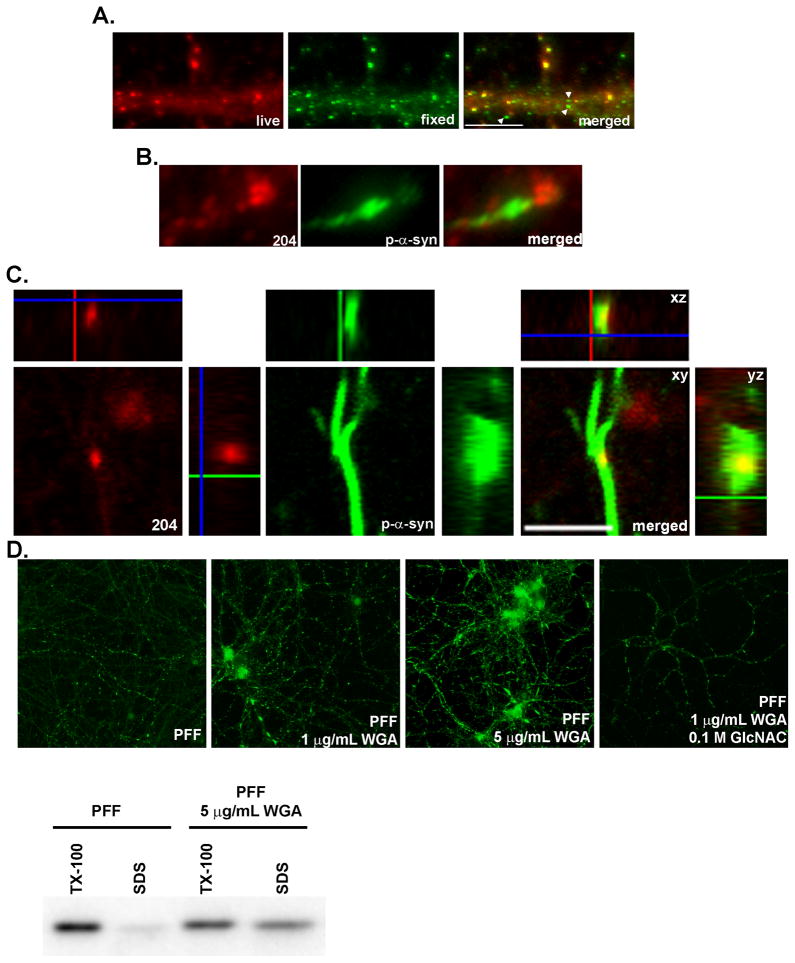
Figure 5. α-syn-hWT pffs are internalized into neurons.
A. Live neurons were incubated with mAB Syn204 (red) to label extracellular α-syn-hWT pffs, followed by fixation, permeabilization and incubation with LB509 (green) to label both intracellular and extracellular α-syn-hWT pffs. Extracellular α-syn-hWT pffs are visualized as yellow in the merged image. Arrowheads highlight examples of internal α-syn-hWT pffs (green). Scale bar = 10 μm. B. Fixed and permeabilized neurons were double labeled with mABs 81A (green) to detect p-α-syn and Syn 204 (red) to detect α-syn-hWT pffs. P-α-syn can be visualized accumulating from seeds of α-syn-hWT pffs. C. α-syn-hWT pffs were added to DIV5 neurons, fixed 14 days later and immunofluorescence was performed to label extracellular α-syn-hWT pffs (red) and p-α-syn (green). A z-stack of confocal images shows that puncta corresponding to α-syn-hWT pffs colocalized with p-α-syn within a neurite, suggesting that pathologic p-a-syn grows from intracellular pffs. D. DIV5 neurons were treated with either α-syn-hWT pffs alone or pffs with 1 μg/mL or 5 μg/mL of WGA. To inhibit WGA endocytosis, neurons were preincubated with 0.1 M GlcNAC followed by incubation with pffs, GlcNAC and 5 μg/mL of WGA. Neurons were fixed 4 days later. Immunoblots and immunofluorescence showed that WGA dose-dependently increased the extent of insoluble p-α-syn.