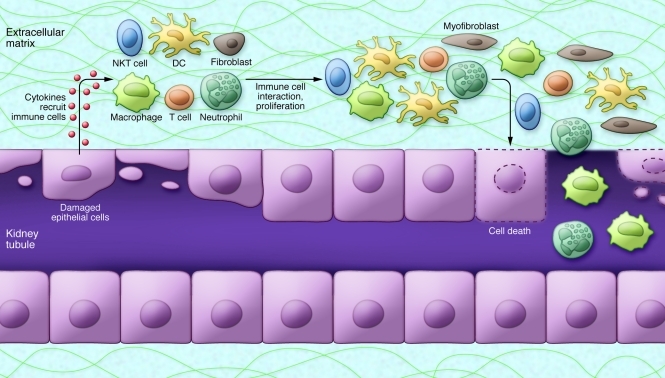
Figure 4. Immune response in ischemic AKI.
The injured tubular epithelium releases proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which aid in recruiting immune cells. Epithelial cells also express adhesion molecules, TLRs, and T cell costimulatory molecules, which activate the immune cells and amplify the inflammatory responses. Neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer T (NKT) cells cause direct injury to tubular epithelial cells. DCs are involved in both the innate and adaptive immune responses through secretion of inflammatory cytokines and presentation of antigens to T lymphocytes.