Figure 2. NMN administration improves impaired glucose tolerance in HFD-induced diabetic mice.
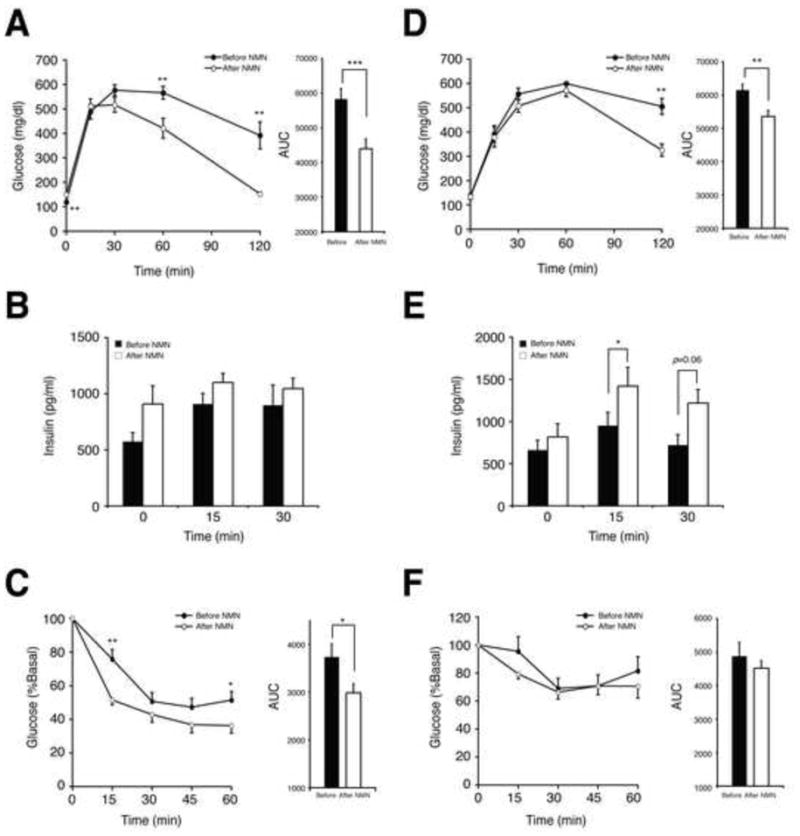
(A and D) Glucose tolerance in HFD female (A) and male mice (D) before and after NMN treatment (n=10 for females, and n=6 for males). IPGTTs were conducted with the same individuals before (closed circles) and after (open circles) NMN. NMN (500mg/kg body weight/day) was administered to female and male mice for 7 and 10 consecutive days, respectively. The areas under each glucose tolerance curve are presented next to the glucose tolerance curves. (B and E) Plasma insulin levels in female (B) and male (E) mice during IPGTTs before and after NMN treatment (n=10 for females, and n=6 for males). (C and F) Insulin tolerance in HFD female (C) and male (F) mice before and after NMN treatment (n=10 for females, and n=6 for males). ITTs were performed before (closed circles) and after (open circles) NMN. ITTs were conducted several days before or after IPGTTs. The areas under each insulin tolerance curve are presented next to the insulin tolerance curves. Data were analyzed by Student’s paired t test. All values are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P <0.01; ***P < 0.001.
