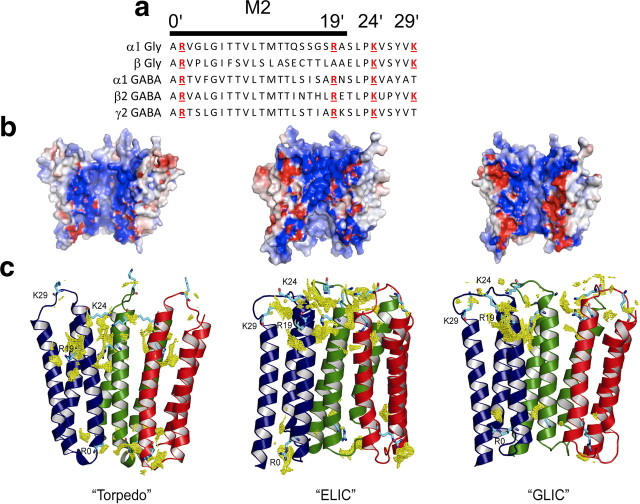
Figure 5.
The channel pore: electrostatic surface potential and chloride density of the interior of the pore in homology models of the α1 GlyR. a, Alignment of residues in M2, the main pore-lining region of glycine and GABA channels. Positively charged residues are highlighted in red. b, Homology models of the α1 Gly homomeric receptor from different templates: the Torpedo receptor (PDB identification number 2BG9; Unwin, 2005), ELIC (PDB identification number 2VL0; Hilf and Dutzler, 2008), and GLIC (PDB identification number 3EHZ; Hilf and Dutzler, 2009). For clarity, the front two subunits of each pentamer have been removed. The electrostatic potential (calculated with PyMOL ABPS) is displayed in a range of −5kT (red) to +5kT (blue). c, Chloride densities for the same homology models (calculated with the program GRID; Goodford, 1985) are shown as yellow meshes. For clarity, only the M1, M2, and M3 helices of three subunits (colored blue, green, and red) are shown. The side chains of positively charged residues (R0′, R19′, K24′, and K29′) are shown in cyan.