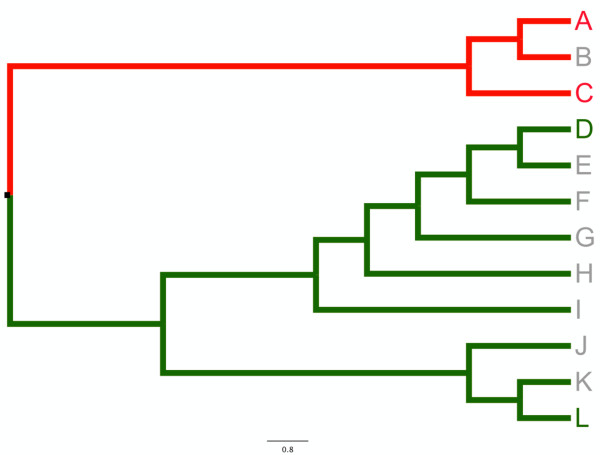
Figure 1.
Sequence selection methods. A sister-pair comprising more speciose (green) and less speciose (red) clades. Coloured taxa indicate those for which sequence data is available. Using our methods, Taxon D is selected for analysis, because its root-to-tip branch is separated from the basal node by 6 nodes, compared to 3 for Taxon L. By contrast Taxon A is selected for analysis using our methods because its root-to-tip branch is separated from the basal node by two internal nodes, compared to one for Taxon C. In both cases, a large component of the sequences are shared by other members of the respective clades over the whole molecular branch length, relative to the sister clade.