Figure 2.
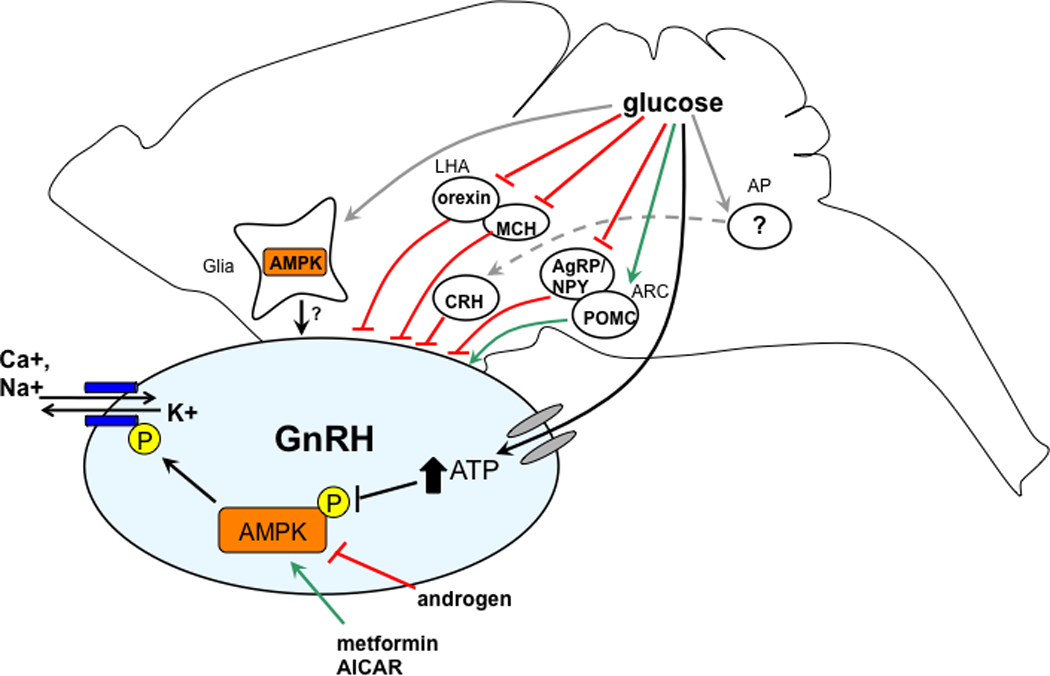
Putative sites of glucose action in the brain to regulate GnRH neuronal function. Glucose may act on distal brain regions in the hindbrain area postrema (AP), and in the arcuate (ARC) and lateral hypothalamus (LHA), which project (both directly and indirectly) to GnRH neurons. In addition, glucose may alter the function of GnRH neurons through direct action mediated by AMPK, or through effects on proximal glial cells.
